In the world of building greenhouses, glass is a top choice. It’s great because it lets lots of light through, lasts a long time, can handle the heat, stays clean, and stops dew from forming. These features make glass the go-to material for many greenhouse experts. This article explores the different types of glass used in glass greenhouses and their key features, helping you build a better commercial greenhouse.
Don’t Miss: 3 Types of Commercial Greenhouse Covering

Essentials for Greenhouse Glass
Picking the right glass for your greenhouse means looking at several factors that affect how well your greenhouse works and how your plants grow. Glass is more than just a barrier; it’s key to controlling the environment for ideal plant growth. Here are some crucial things to consider when choosing greenhouse glass:
1. Light Transmittance
Plants need light for photosynthesis, which is all about the quality and amount of light. Glass with high light transmittance makes sure your plants get plenty of sunlight, boosting their growth and yield. This leads to healthier plants and more harvest. There are three main types of glass based on light transmittance: 90.5%, 91.5%, and 97.5%. The 90.5% is typical ultra-clear tempered glass, 91.5% is ultra-clear diffuse glass, and 97.5% is ultra-clear anti-reflective glass.

Ultra-clear anti-reflective glass is best for increasing yields but costs more. It’s mostly used in experimental and seedling greenhouses. Ultra-clear diffuse reflective glass, cheaper and widely used in planting greenhouses, is the standard in the industry. Ultra-clear tempered glass, less common, is often replaced with the diffuse type during greenhouse upgrades.
2. Strength
Greenhouse glass needs to be tough against nature’s challenges, like strong winds and heavy rain. Strong glass protects plants from bad weather and cuts down on repair and replacement, saving money and time. Many modern greenhouses use tempered glass, which is very strong and can last over 20 years.
3. Insulation
Good insulation glass keeps the greenhouse warm, no matter the weather outside. This creates a perfect environment for plants, reduces energy use, and cuts costs. For the walls of our greenhouses, we usually use standard insulated float glass to insulate better and keep the warmth in.
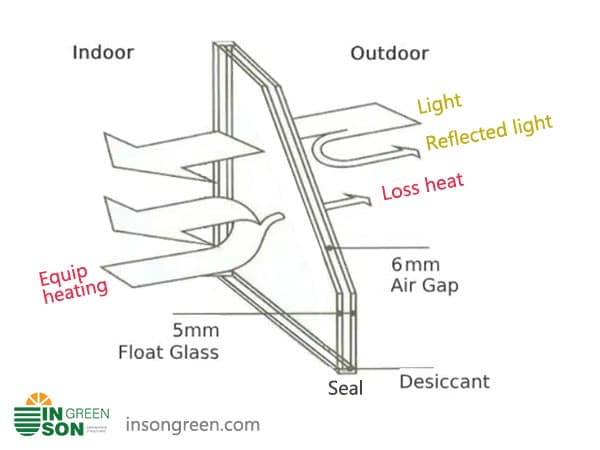
4. Scattering
Scattering is about spreading sunlight evenly inside the greenhouse. It’s crucial everywhere. In sunny places like the Middle East, scattering glass spreads light evenly, reducing stress on plants from direct sun and lowering leaf temperature by about 5 degrees Celsius. It’s also great in places like Africa, preventing crops from getting too much sun. In colder, less sunny areas, scattering helps plants get enough light.
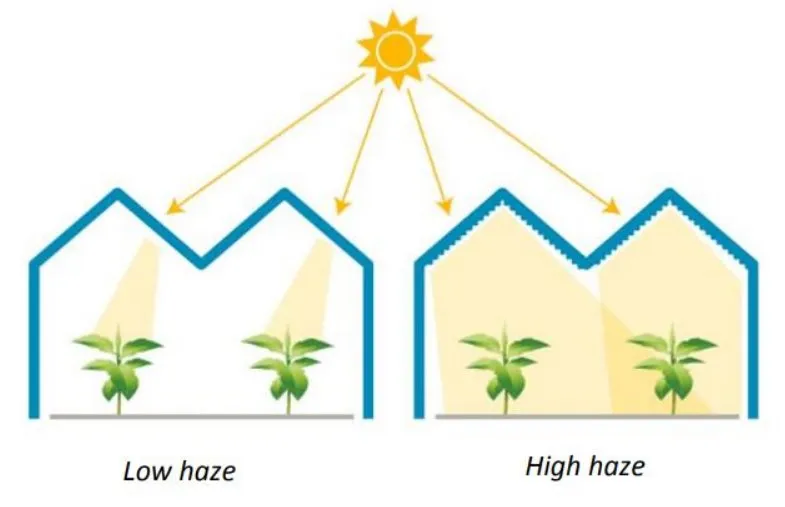
4. Haze Value
The haze value depends on the climate where the greenhouse is. It adjusts the strength of light through the glass. In sunny places like the Middle East and Africa, high haze value glass lowers light intensity to keep crops safe. In colder, darker areas, a lower haze value is better to use as much sunlight as possible.
5. Light Transmission Over Time
Over time, the way you clean and use high-transmitting glass can change how much light it lets through. For example, rough cleaning can wear down the glass coating, reducing light. Etched anti-reflective glass, which is more durable, keeps its light transmission almost the same for about 20 years. This means it stays effective even after long use.
What Type of Glass is Used for Greenhouses?
When building a glass greenhouse, choosing the right frame and glass is crucial.
1. Greenhouse Frame
We use top-notch aluminum profiles designed specifically for greenhouses. The main structure is built from 6061 high-strength aluminum alloy. It’s treated for surface protection, adhering to national standards. This makes our aluminum frames strong and perfect for greenhouses. They are crafted by professional manufacturers.

2. Greenhouse Side Wall Glass
The side walls of the greenhouse typically use standard 5mm+6A+5mm insulated float glass. Since a lot of heat escapes through the greenhouse walls and leaks in winter (70-80% of total heat loss), enhancing the insulation and sealing of the structure is key. This approach effectively reduces heat loss and is cost-efficient.

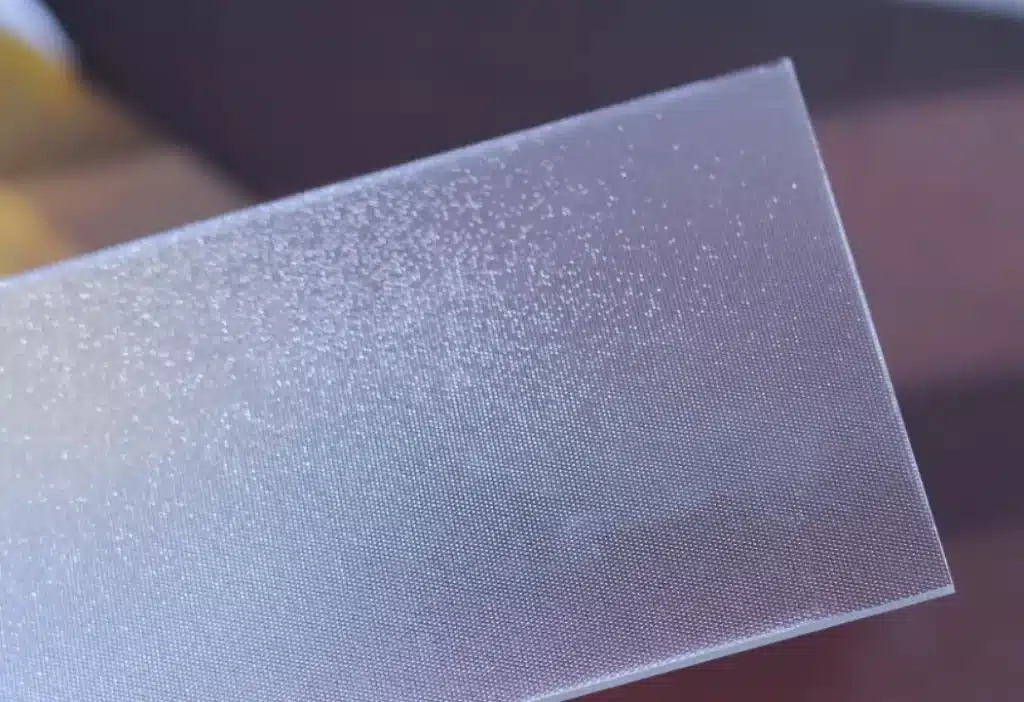
3. Greenhouse Roof Glass
For the roof, we prefer 4mm tempered scattering glass with over 91.5% light transmittance. This glass, combined with special aluminum profiles and durable rubber seals, offers excellent sealing and looks great. Tempered glass boasts amazing strength and break resistance.

Greenhouses, usually 5-7 meters tall, are often used for vertical farming of fruits, vegetables, flowers, and medicinal plants. Safety is a top priority for such tall structures, especially the roof glass. Tempered glass is essential to prevent accidents during severe weather.
Another important factor is light scattering. Controlling temperature is vital for year-round farming and impacts operational costs. The 4mm tempered scattering glass, with up to 97.5% light transmittance, ensures enough light without the risk of underexposure. It softens sunlight, preventing leaf burn in plants, and can reduce indoor temperatures by about 5 degrees Celsius in summer.
We choose tempered scattering glass with varying haze values to suit different light and temperature conditions.
4. Standard Technical Parameters for Our Glass Greenhouses:
- Roof Glass: 4mm/5mm tempered scattering glass
- Side Wall Glass: 5mm+6a+5mm/4mm+9a+4mm standard insulated float glass
- Heat Transfer Coefficient: 3.3W/m2°C
- Light Transmittance: >91.5%
- Impact Test: No breakage or cracks
- Softening Temperature: 200°C
- Climate Aging Test: 5000 hours with only a 0.1% decrease in light transmittance
- Service Life: Over 25 years
Greenhouse Glass FAQs
FAQ 1: How thick should the glass be for a greenhouse?
The right glass thickness for a greenhouse varies. It depends on where you’re located, the weather, what your greenhouse needs structurally, and your budget. The usual choices are 4mm and 5mm.
For example, 4mm tempered scattering glass is great for greenhouse roofs because it’s strong and lets plenty of light through. For the sides, 5+6+5mm insulated float glass works best, offering top-notch insulation.
FAQ 2: What is the most efficient greenhouse glass?
The best greenhouse glass has high light transmission, scatters light well and insulates effectively. Ultra-clear anti-reflective glass is a top pick because it lets through 97.5% of light, boosting light efficiency. Glass that scatters light evenly is also great. It reduces the stress of direct sunlight on plants and keeps leaf temperatures lower.
FAQ 3: Do greenhouses use normal glass?
Regular glass, like the kind in homes or stores, isn’t ideal for greenhouses. Greenhouse glass needs to let lots of light through, resist impact, last long, and have special scattering or reflective qualities. Even when a greenhouse uses normal float glass-like material, it’s usually treated (like being tempered or coated) to meet the unique light and weather demands of greenhouses.
Conclusion
This article covered different greenhouse glass types and their important features. Picking the right glass is essential for your plants to grow well and for your greenhouse to be cost-effective and sustainable. Knowing and choosing the right glass is key, no matter your location or climate.
Thinking of building a greenhouse? Reach out to us at INSONGREEN. We specialize in high-quality commercial greenhouses, offering expert design, support, and installation. Our team is committed to delivering an efficient, budget-friendly greenhouse for you.





