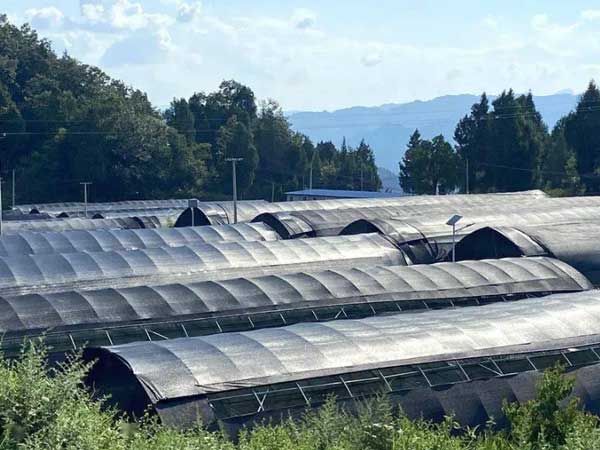
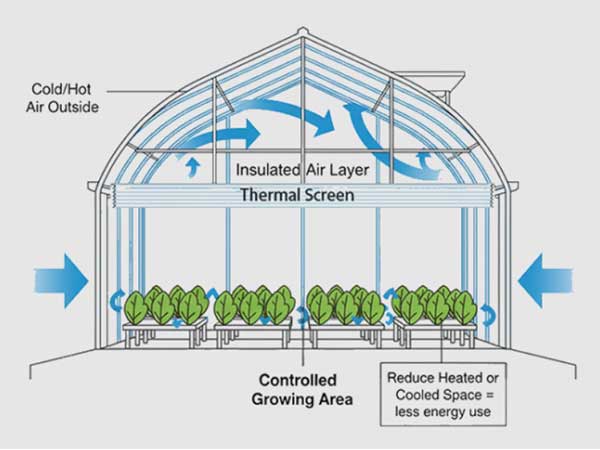
Greenhouse technology has become critical for improving crop yield and quality and enabling year-round production. However, glass or polycarbonate panel greenhouses often come with high costs, making them less accessible for small-scale farmers and agricultural startups. In contrast, poly film greenhouses offer a flexible and budget-friendly alternative.
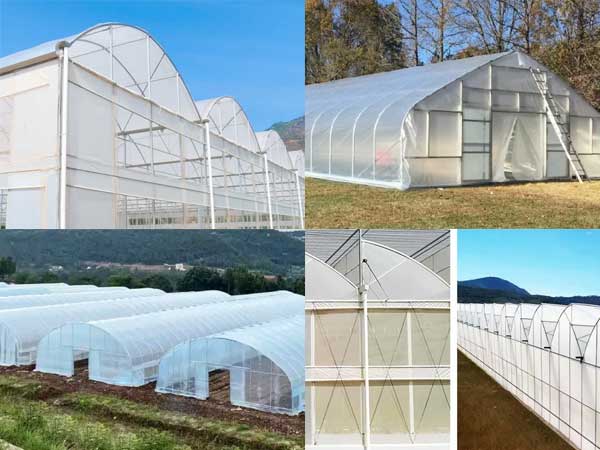

Far from being a “low-end” option, poly film greenhouses are gaining popularity due to structure and material innovation advancements. This article delves into the definition, advantages, common types, and ideal applications of poly film greenhouses, aiming to provide comprehensive guidance for agricultural practitioners.
Don’t Miss: Poly Tunnel vs Greenhouse: Which is Better for Your Crops?
What is a Poly Film Greenhouse?
A poly film greenhouses is a lightweight greenhouse structure covered with polyethylene (PE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or modified ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) films. Its framework often utilizes galvanized steel pipes, aluminum alloys, or bamboo structures. Similar to other greenhouses, these can be designed as standalone units or multi-span constructions. Roof styles vary and include options like sawtooth and hoop, with the polytunnel-style hoop design being particularly popular.
Why Use Plastic Films as Greenhouse Covers?

The extensive use of plastic films for greenhouse coverings is no accident. Their unique properties make them an economical and practical choice for agricultural applications. The rise of poly film greenhouses is closely linked to several key advantages:
- High Light Transmission: Quality plastic films can achieve 80-90% light transmission rates, which is sufficient for most crops’ photosynthesis needs. Advanced films also include UV resistance, anti-drip, and light diffusion features through surface coatings, optimizing the growing environment for plants.
- Cost-Effectiveness: With low production and replacement costs, plastic films are much more economical than glass or polycarbonate sheets. They are the first choice for reducing initial investments for large-scale greenhouse construction.
- Flexibility: Plastic films can accommodate various terrain and usage scenarios, whether as single or multi-layer covers. They are suitable for short-term seasonal use and longer planting cycles, demonstrating their versatility.
Don’t Miss: Best Greenhouse Covering – Plastic Types >>
Poly Greenhouse Benefits
The unique properties of poly film make these greenhouses an essential choice for agricultural production. Below are the primary advantages:
1. Cost-Effective
Compared to the high costs of glass greenhouses, which can reach several hundred dollars per square meter, poly film greenhouses cost only about a third of that
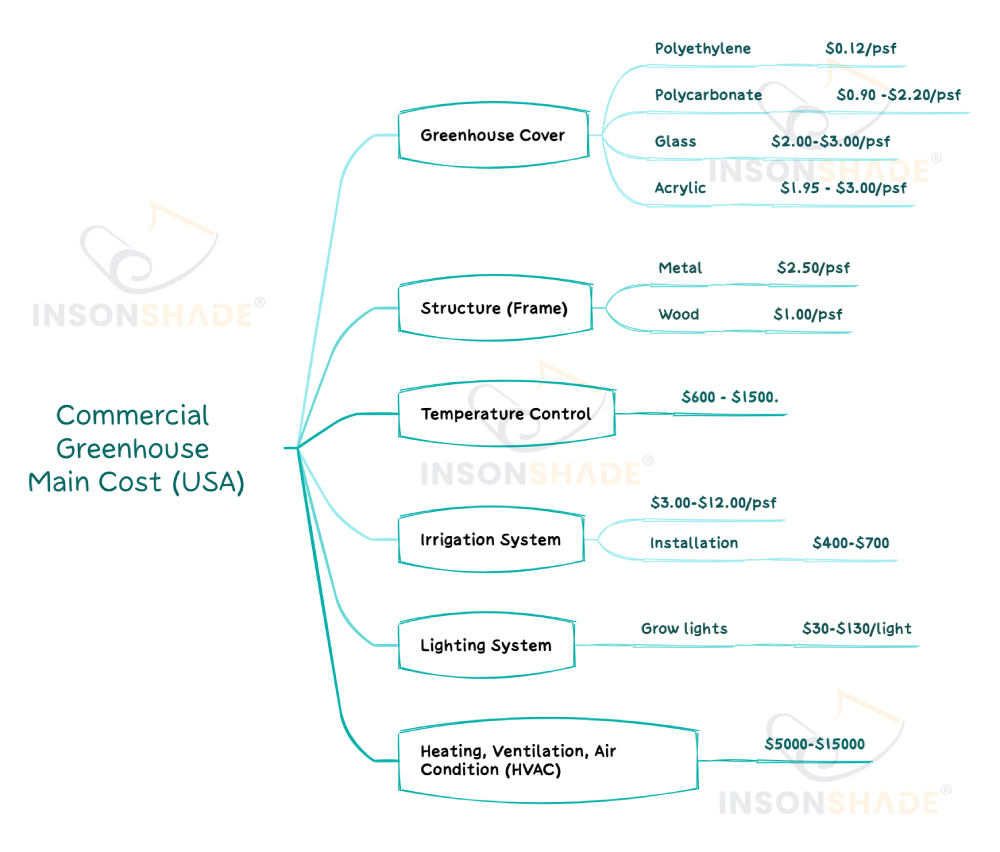
or even less. This affordability allows farmers to scale production rapidly with limited funds, making it particularly suitable for agriculture startups.
2. Easy Installation and Maintenance
Poly film greenhouses are easy to install and do not require advanced machinery or skilled labor. Additionally, if the film is damaged, it can be replaced quickly and at a low cost, ensuring minimal disruption to large-scale farming operations.
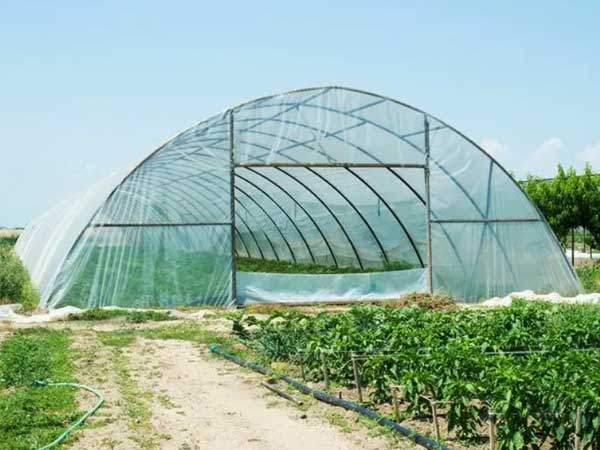

3. Versatile Applications
Poly film greenhouses are suitable for various climates. They can provide shade and cooling in tropical regions while offering heat retention in colder areas, making them adaptable to different agricultural needs worldwide.
Poly Film Greenhouse Challenges
While poly film greenhouses are favored for their cost-effectiveness and flexibility, they also have certain limitations in terms of durability and environmental control. These drawbacks must be considered during planning and usage to ensure long-term viability. Below are the key challenges:
1. Limited Durability
Even high-quality films typically last only 3-5 years, while standard films may degrade within 1-2 years. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation accelerates aging, reduces light transmission, and diminishes insulation and overall performance. Additionally, the films are susceptible to mechanical damage and harsh weather conditions, requiring frequent replacement and increasing maintenance costs.
2. Precision in Environmental Control
Poly film greenhouses provide basic control over temperature and humidity but fall short in critical areas such as light intensity, airflow distribution, and humidity stability. Compared to smart glass greenhouses or premium polycarbonate (PC) panel greenhouses, poly film structures are less capable of meeting the stringent environmental requirements for high-value crops or experimental planting projects.
3. Increased Long-Term Operating Costs
Although the initial construction cost of a poly film greenhouse is low, maintenance and operational expenses can accumulate over time. Frequent film replacements and the need for supplemental heating equipment in colder regions can lead to significantly higher energy and upkeep costs in the long run. This is especially true in areas where environmental stability is critical.

4. Limited Aesthetic Appeal and Weather Resistance
Poly film greenhouses are designed primarily for functionality and often lack aesthetic appeal. This makes them more suited for practical agricultural projects rather than ornamental purposes. Moreover, their resistance to wind and snow loads is relatively weak. Additional supports and reinforcements are necessary in regions with high wind or heavy snowfall, increasing costs and construction complexity. Without these measures, the structure may face damage or collapse risks.
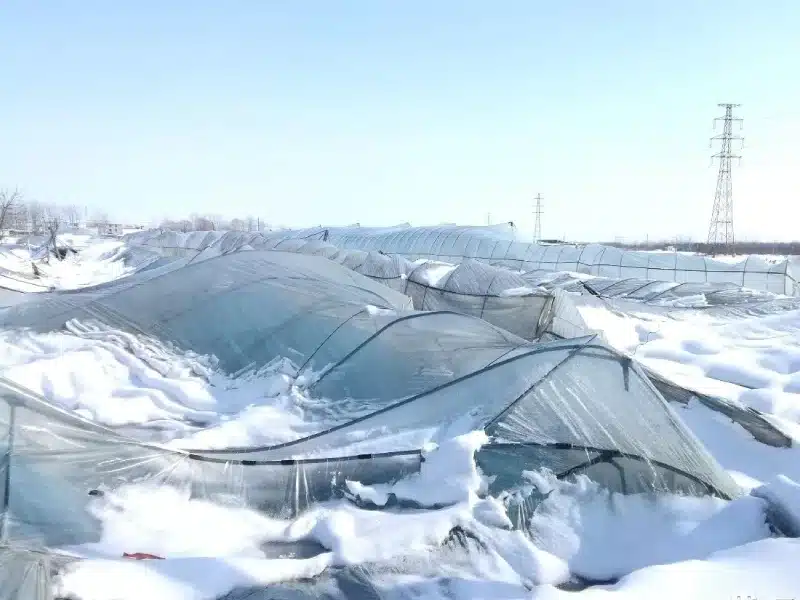

Poly Film Greenhouse Types
Poly greenhouses can be classified into several types based on their structure and purpose. Each type has unique characteristics in terms of cost, functionality, and suitability for different applications. Below are the main types of poly film greenhouses:
1. Free-Standing Polytunnel
The free-standing polytunnel is one of the most common types of poly film greenhouses. It comes in two variants: low tunnel and high tunnel. Its overall structure is simple, and its cost is the lowest among greenhouse types.
A low polytunnel is typically used for small-scale seedling cultivation or home gardening. Its hoop structure can be made from PVC pipes, aluminum alloys, or bamboo.
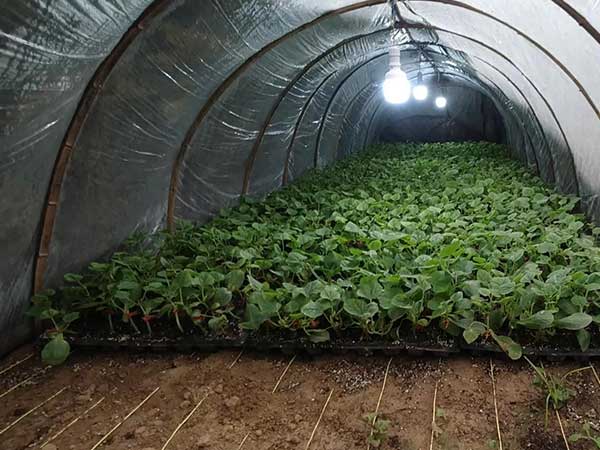

On the other hand, commercial heavy-duty high tunnels usually use arched steel pipes as the framework and are covered with single or multiple layers of film. They are suitable for temporary commercial planting projects.
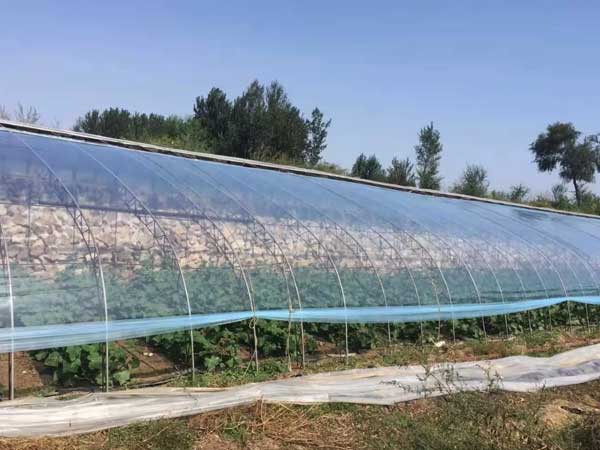

Due to the limited insulation performance of this type, it usually only provides basic heating environments. To achieve better thermal insulation, improved designs with double or multi-layer arches are adopted in colder regions.
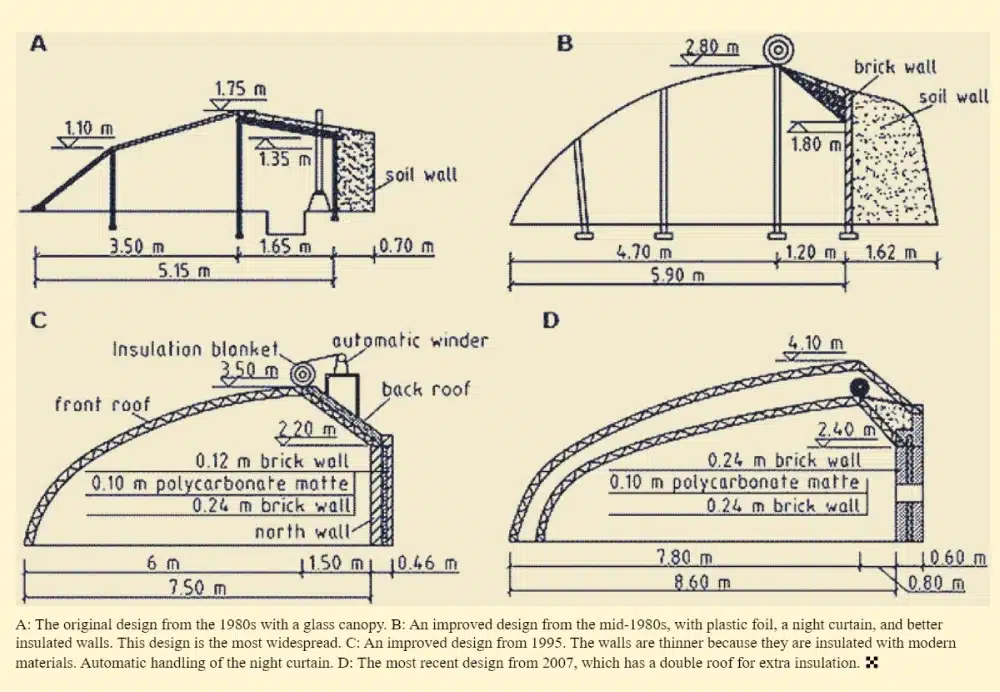
2. Multi-Span Poly Greenhouse
The multi-span poly greenhouse connects multiple single-span tunnels using gutters and supporting structures to form a large-scale, unified greenhouse.
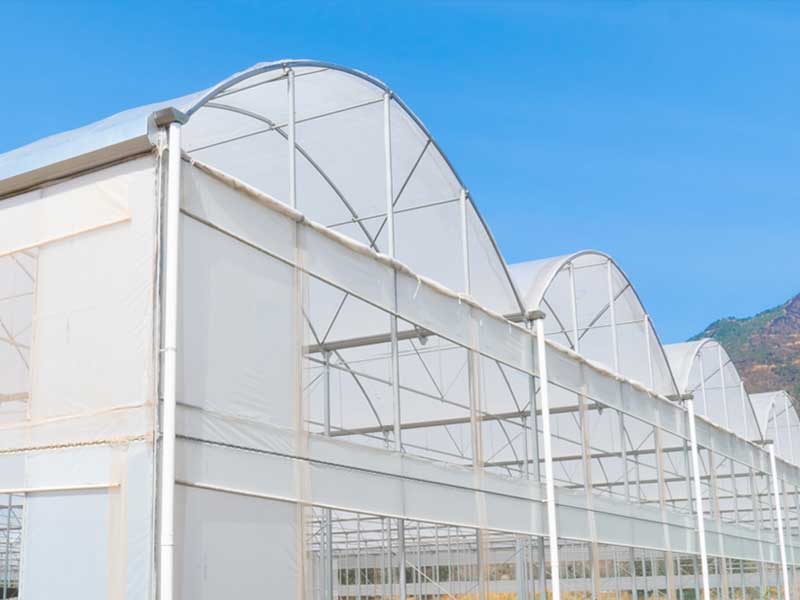

This design significantly increases usable space, facilitates the introduction of mechanized operations, and improves production efficiency. The interconnected structure also allows for easier internal environment management, enabling precise control of temperature, humidity, and lighting. Multi-span greenhouses are ideal for large-scale vegetable, flower, and cash crop production. Although their initial construction cost is higher than that of single-span tunnels, the long-term economic benefits and return on investment make them an excellent choice for commercial agriculture.
3. Inflated Film Greenhouse
The inflated film greenhouse uses air blown between two film layers to create a stable air cushion. This design significantly improves thermal insulation and enhances wind resistance, making it suitable for harsher climatic conditions.
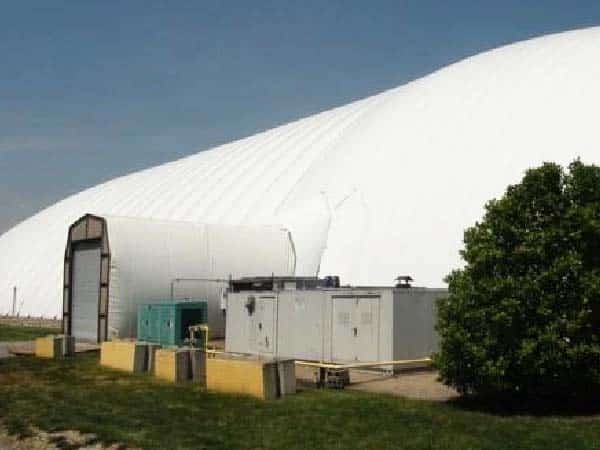

With its excellent heat retention, this type of greenhouse is particularly well-suited for growing vegetables and fruits in cold regions. The inflated film design also reduces heat loss, making it advantageous in areas with high energy costs. It is an ideal solution for agricultural operations in extreme cold environments.
4. Specialized Modified-Film Greenhouse
Specialized modified-film greenhouses utilize high-performance plastic films, such as UV-resistant and highly light-transmissive PO films. These advanced films greatly improve weather resistance and light efficiency.
This type of film reduces the adverse effects of UV rays on crops while optimizing uniform light distribution to promote photosynthesis. Specialized greenhouses with strict light requirements are commonly used for cultivating high-value crops, such as tomatoes and strawberries. Additionally, the durability of these films reduces the frequency of replacements, lowering maintenance costs. They are a key choice for agricultural projects to maximise yield and efficiency.
Poly Film Greenhouse Applications
Polyethylene (PE) film greenhouses are widely used in various agricultural scenarios due to their flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Below are the primary use cases.
1. Startup Agricultural Projects
For farm owners or agricultural startups with limited budgets, poly film greenhouses provide an ideal low-cost solution for quick deployment. Compared to glass or polycarbonate greenhouses, these structures require significantly lower initial investment and have shorter construction times. They enable farms to establish a rapidly protected growing environment, helping entrepreneurs enter the market swiftly. This makes them particularly suitable for small-scale cultivation, high-value crop experiments, or early expansion phases of agricultural businesses.
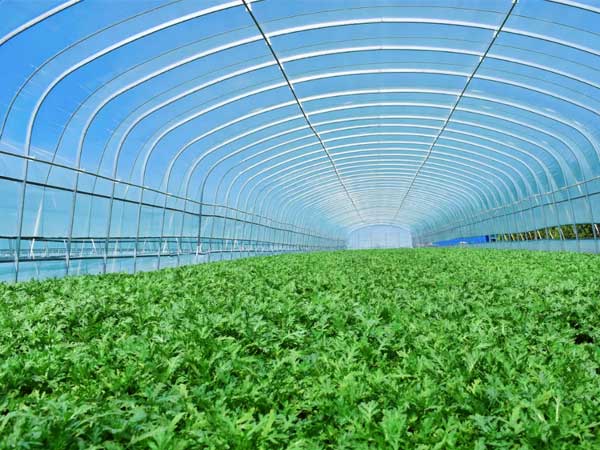

2. Seasonal Crop Protection
Poly film greenhouses are crucial in seasonal cultivation, especially for short-term crop protection during early spring or late autumn. In cooler weather, these greenhouses offer adequate heating and insulation to ensure the normal growth of crops. With their low construction and maintenance costs, they minimize financial waste associated with temporary usage, providing a practical solution for adapting to climate changes and extending growing seasons.
3. Rapid Seedling Facilities
In producing flowers, fruits, vegetables, and seedlings, poly film greenhouses create an optimal environment for temperature and humidity control during the seedling phase. This stage requires effective insulation and protection from wind and rain, which poly film greenhouses efficiently provide at a fraction of the cost of other greenhouse types. The flexibility and quick setup of these greenhouses are particularly advantageous for seedling producers who require frequent crop rotations.
4. Agricultural Development in Extreme Environments
Poly film greenhouses also demonstrate exceptional adaptability to harsh climate conditions. In tropical regions, they offer shading and cooling functions, protecting crops from high temperatures and intense sunlight. In colder regions, thicker films or double-layer inflated designs enable effective heating and insulation, ensuring crop growth in freezing conditions. The flexible design and potential for localized modifications allow poly film greenhouses to support agricultural breakthroughs in challenging environments, promoting development in these areas.
Conclusion
Polyethylene film greenhouses are far from being merely a “cheap alternative.” These greenhouses can meet essential environmental protection needs for agricultural projects involving high-value crops while integrating advanced automation and smart technologies to enhance environmental control. For instance, poly film greenhouses can have intelligent temperature and humidity sensors, automatic film rolling systems, and precise irrigation devices. These features enable real-time monitoring and adjustment of the greenhouse’s light, temperature, and humidity conditions, creating the best possible crop growth environment.
If you’re considering purchasing a modern poly film greenhouse, feel free to contact us to learn about the latest factory pricing.