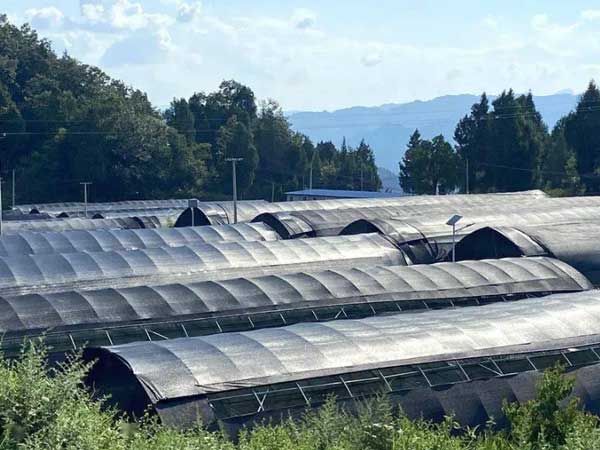
The greenhouse is very useful for growing high-quality grapes. It acts like a tailor-made “safe haven” for your grapes, helping you effortlessly manage harsh weather and pesky insects across different seasons and regions. According to ScienceDirect, greenhouse grapes are more profitable than open-field grapes due to their premium prices. So, investing in a commercial greenhouse for grape cultivation seems like a great idea. But how can you effectively grow grapes in a greenhouse?
In this article, I will guide you step-by-step on how to successfully grow grapes in a greenhouse, from selecting the right varieties to harvest management, along with essential pest and disease control knowledge. Ready to get started? Let’s dive in!
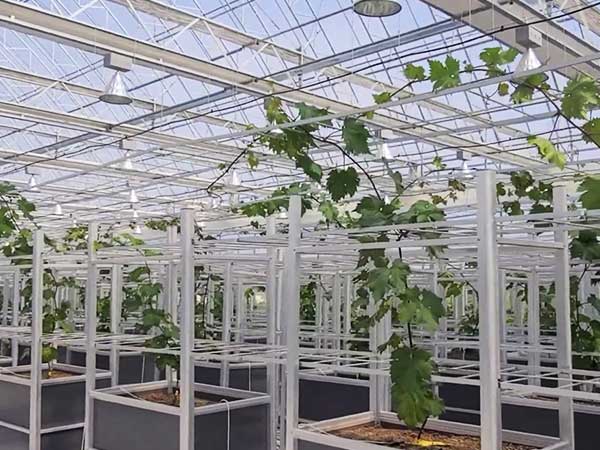

Part 1: Choosing the Right Grape Varieties for Greenhouse Cultivation
Want to grow grapes in a greenhouse? Choosing the right variety is the first step! By 2024, FPS has recorded 565 grape varieties, but not just any variety will thrive in a greenhouse. Typically, grapes that are heat and humidity tolerant, early-ripening, and self-pollinating are the best choices.
Additionally, the preferred varieties differ depending on the region. For example, in the UK, Black Hamburgh, Muscat of Alexandria, and Chasselas are popular for greenhouse cultivation. In the USA, Thompson Seedless, Flame Seedless, and Red Globe are top choices. Canadian greenhouse growers favor cold-resistant varieties like Sovereign Coronation, Himrod, and Lakemont. In China, popular varieties include Victoria, Beauty Finger, Gold Finger, Sunshine Rose, Early Kyoho, and Seedless White.
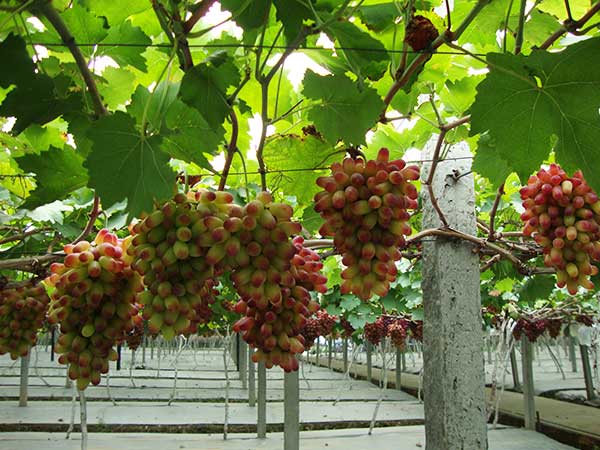

The same variety may have different names in different countries. But the varieties you choose will share a common trait: they thrive in greenhouses, produce high-quality fruits, and fetch a good price in the market. So, picking the right “star” variety not only ensures high yields and quality but also significantly boosts your economic returns.
Part 2: Greenhouse Construction and Preparation
Once you’ve selected the grape varieties, the next critical step is greenhouse construction and preparation.
1. Greenhouse Design and Construction
First, the greenhouse design must fully consider the growth needs of grapes.
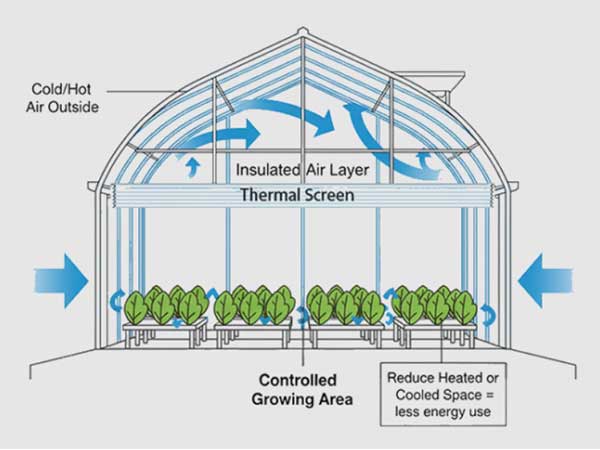
For instance, grapes love sunlight, so it’s best to build your greenhouse facing the sun. If you’re in the Northern Hemisphere, a south-facing orientation is ideal because sunlight is the primary energy source for a greenhouse. Secondly, the greenhouse structure must be sturdy to withstand adverse weather conditions such as summer storms or hail. Finally, various systems such as ventilation, temperature control, humidity control, and irrigation need to be configured according to your budget and local climate conditions to ensure that grapes receive ideal growing conditions at every stage of their growth.
Don’t Miss: 18 Types of Commercial Greenhouse
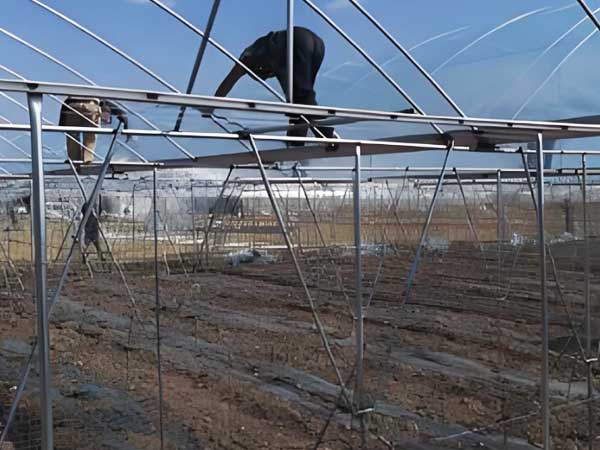

2. Light Management
Although grapes love sunlight, excessive light in summer can harm them. Therefore, it’s recommended to install shading nets or cloths to control light intensity. Proper lighting will give your grapes an attractive appearance and high sweetness.
3. Soil Preparation
Grapes are adaptable to various soils but prefer sandy loam or light loam rich in organic matter and well-drained soil. Before planting, it’s advisable to deep plow the soil and add organic fertilizers to enhance soil fertility. The soil pH should ideally be between 6.0 and 6.5, which better meets the growth needs of grapes.

Part 3: Planting Grape Seedlings
With the greenhouse prepared, it’s time to plant your grape seedlings. This process involves choosing the right planting time, employing proper planting methods, and managing the seedlings scientifically to ensure healthy growth from seedlings to mature plants. Let’s break it down step by step.
1. Planting Time
While the greenhouse environment allows more flexibility with planting time, we usually recommend planting in late winter or early spring. During this period, the temperature in the greenhouse is lower, which is conducive to root establishment and dormancy, preparing the seedlings for the upcoming growing season.
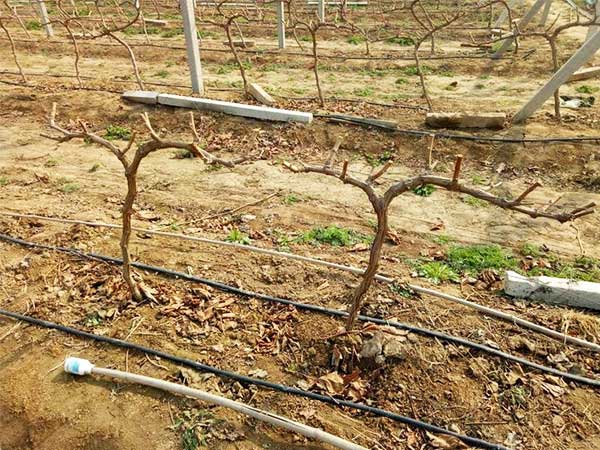

2. Planting Method
When planting, transplant the seedlings into the prepared soil, making sure the roots are fully covered and gently pressed to ensure good soil contact. The recommended plant spacing is 1.5 to 2 meters between plants and 2 to 3 meters between rows. Proper spacing not only supports grapevine growth but also ensures good air circulation and even light distribution, reducing the risk of disease.
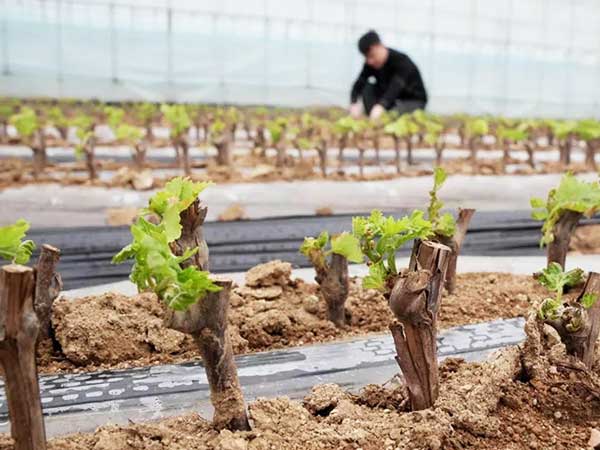

3. Seedling Management
After planting, the focus shifts to managing the seedlings. Irrigation and fertilization are particularly important at this stage. A drip irrigation system is recommended to ensure even water penetration to the roots, avoiding waterlogging that can damage the root system. As for fertilization, applying an appropriate amount of nitrogen fertilizer can promote rapid growth and leaf development. Liquid fertilizer should be applied every 2 to 3 weeks to provide consistent nutrient support to the seedlings.
With comprehensive management in these three areas, you’ll lay a solid foundation for the healthy growth of your grapes, ensuring strong plants and preparing for a bountiful harvest.
Part 4: Vine Management
After the seedling stage, vine management begins, which is crucial for ensuring large, sweet grapes. This phase focuses on three key aspects we’ll discuss below. Proper vine management not only improves grape growth but also enhances photosynthesis, promoting healthy fruit development.
Part 5: Building a Trellis System
The trellis system is the “skeleton” of greenhouse grape cultivation. Typically, after the greenhouse is built and grape seedlings are planted, you can start building the trellis system based on the growth of the seedlings. The trellis height is usually between 2 to 2.5 meters, allowing the grapevines to fully utilize vertical space. The trellis must be strong enough to support the weight of the vines and the future bountiful fruits. Additionally, the design should consider ventilation and light exposure, ensuring each leaf gets enough sunlight and fresh air, which helps reduce the risk of disease.
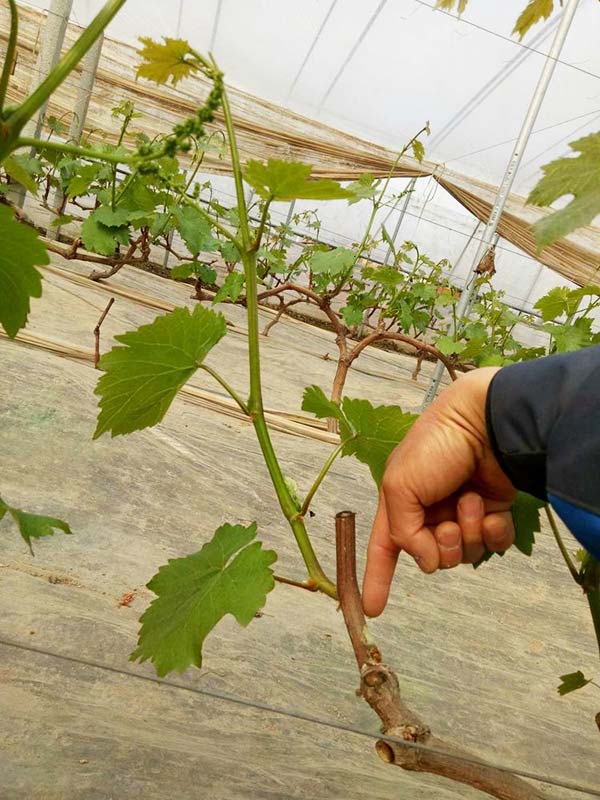

1. Pruning and Trimming
Grapes are vining plants, so pruning and trimming are essential. Winter is the best time for pruning as the grapes are in a dormant state, making it ideal for adjusting branch density. Pruning aims to control the plant shape, avoid nutrient dispersion, and improve ventilation and light conditions, ultimately helping the grapes produce sweeter fruits. For detailed pruning techniques, you can refer to the Royal Horticultural Society’s guide.
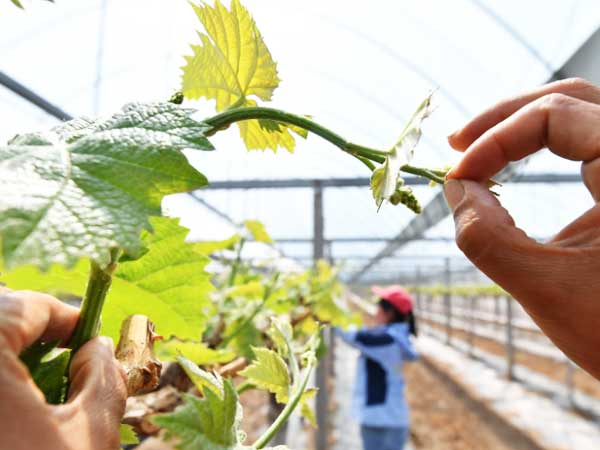

2. Training Grape Vines
In addition to building a trellis and pruning, training the grapevines is also important. Through training, you can guide the grapevines to grow evenly along the trellis, preventing them from crowding, which blocks light and encourages mold and disease. Regularly check and adjust the direction of vine growth to ensure each branch receives ample sunlight, promoting faster and healthier growth.

Overall, by following these scientific steps, you can create ideal growing conditions for your grapes, ensuring they produce high-quality, high-yield fruits that will lead to a bountiful harvest.
Part 6: Managing the Growing Season
As the grapes enter the growing season, temperature, humidity, and light management become crucial. Maintain daytime temperatures in the greenhouse between 22°C and 28°C (72°F to 82°F) and nighttime temperatures between 15°C and 20°C (59°F to 68°F). Humidity should ideally be between 50% and 70%, which is beneficial for pollen maturation and pollination. During the flowering period, you and your staff should gently shake the grape stems to assist with pollination.
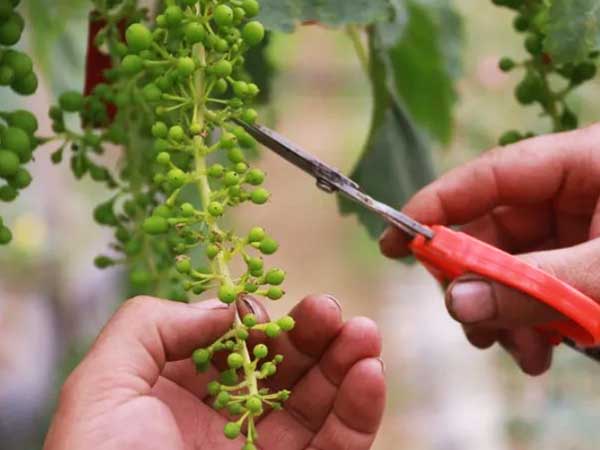

Ensure the grapes receive at least 6-8 hours of sunlight each day. If there is insufficient natural light, consider using supplementary lighting, especially during the early morning and late afternoon of the growing season. In the summer, use shading nets to prevent leaf burn.
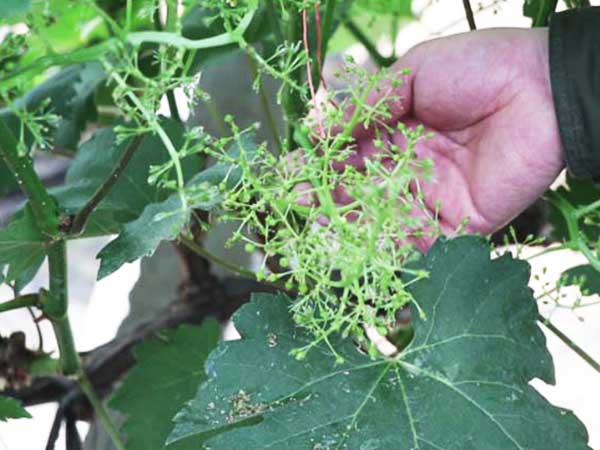

Part 7: Fruit Management and Harvesting
When it comes to fruit management, your goal is to turn all the effort you’ve put in so far into a sweet harvest. This phase requires careful management of sugar accumulation, fruit enlargement, color change, and harvest timing to ensure high-quality, high-yield grapes that command a premium price and have a longer shelf life.
1. Fruit Enlargement and Sugar Accumulation
At this stage, the grapes start to rapidly absorb nutrients and swell like little balloons. Remember to reduce nitrogen fertilizer and increase phosphorus and potassium to speed up fruit maturation and boost sugar levels. Continue using the drip irrigation system, but reduce the water amount slightly, as drier conditions will result in sweeter grapes.

2. Color Change Management
When your grapes begin to change color, it’s a sign they are nearing maturity. At this time, reduce or even stop irrigation for a period to help with sugar accumulation and skin coloration. During this phase, keep an eye on the vines, prune leaves moderately to ensure adequate sunlight exposure, and produce evenly colored, sweeter grapes.
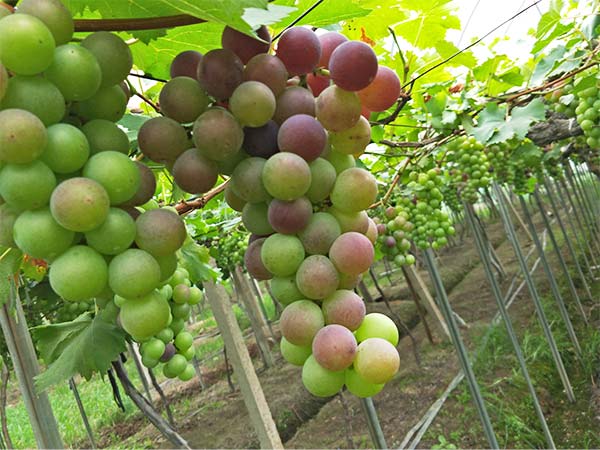

3. When to Harvest Grapes
This is a real art. When the sugar-acid ratio is right, the skin is bright, and the fruit feels firm yet slightly soft, it’s time to harvest. Hand-picking is the best method, as it protects the delicate skin of the grapes and ensures that each grape remains intact.

4. Post-Harvest Handling
If your grapes are destined to become wine or other processed products, send them to the processing plant as soon as possible. If they are to be sold as fresh fruit, perform pre-cooling and then store them in a cold place to prolong freshness, so customers receive grapes as fresh as the moment they were picked.

To sum up, if you follow these steps, your greenhouse grapes will not only yield high quantities and quality but also stand out in the market, bringing you substantial profits!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Successfully growing grapes in a greenhouse comes with challenges like pest control, and temperature and humidity management.
FAQ1: How to Control Pests and Diseases?
Grapes have their own enemies—various pests and diseases. If you want to effectively combat them, check out professional resources that are more reliable than any advice I could give. Here are some authoritative websites you can visit for detailed control methods:
- University of California – Agricultural Pest Management Guidelines
- University of Massachusetts – Grape Pest Management Tablet
- Royal Horticultural Society – Grapevine diseases
FAQ2: Grape Growth Temperature and Humidity Management Chart
| Stage | Temperature Range (°C) | Humidity Range (%) |
| Budding Stage | 15-20°C raised to 20-25°C | >90% |
| Flowering Stage | 25-28°C | 50%-70% |
| Fruit Maturation | Not exceeding 35°C | 50%-70% |
Conclusion
Growing grapes in a greenhouse involves careful planning from variety selection, trellis construction, to temperature and humidity control, and fruit management. Scientific management ensures not only high yield and quality but also maximizes your economic returns. If you’re looking for more efficient help during your grape cultivation journey, feel free to leave a comment.
Of course, we offers commercial greenhouse solutions worldwide. If you need to build a modern greenhouse, you can directly provide your greenhouse requirements to us. We will offer comprehensive support, from greenhouse construction to intelligent environmental control systems, helping you grow high-quality grapes and achieve a bountiful harvest.