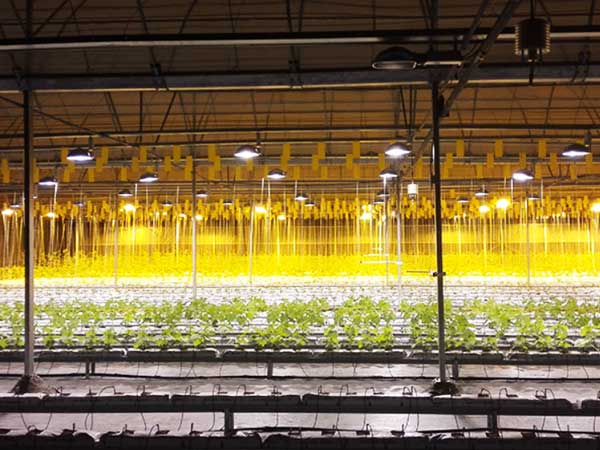
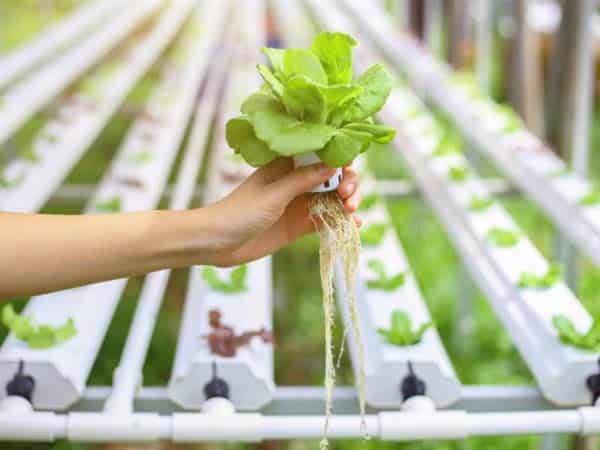
Growing lettuce in a greenhouse offers the benefit of a controlled environment, free from the impact of external weather conditions, allowing for year-round production. This method increases both yield and quality while reducing the risks of pests and diseases.
In 2022, lettuce contributed nearly one-fifth of the $21.8 billion revenue in the U.S. vegetable market. Globally, lettuce also shows immense economic potential. In 2018, the total harvested area exceeded 1.27 million hectares, with a production of about 27.3 million tons. The estimated value of lettuce per acre was around $10,400, highlighting its significant economic returns.
In this article, I’ll guide you through the entire process of growing lettuce in a greenhouse. From preparation, seeding, and media setup to planting and harvesting, these steps will help you maximize the potential of your greenhouse and achieve higher profits.
Part 1: Preparing
1. Choosing and Preparing the Right Greenhouse
Selecting the right type of greenhouse is crucial for growing lettuce. Common choices include film-covered greenhouses, glass greenhouses, and polycarbonate greenhouses, each offering unique benefits. If you’re a beginner or want to experiment with a small garden, a mini greenhouse will suffice, especially for overwintering lettuce.
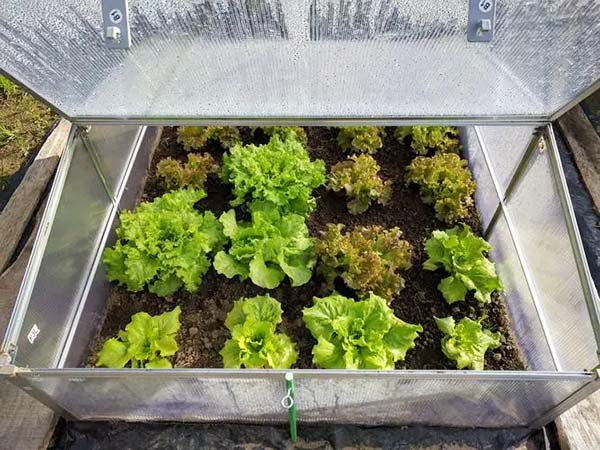

For larger-scale production, you might consider a commercial greenhouse. The cost of such greenhouses can vary greatly, from affordable polytunnels to expensive smart glass greenhouses. It’s recommended to choose a greenhouse type that matches your local environment and the value of your lettuce crops. For example, if your area has highly sandy soil, a hydroponic greenhouse might be necessary.
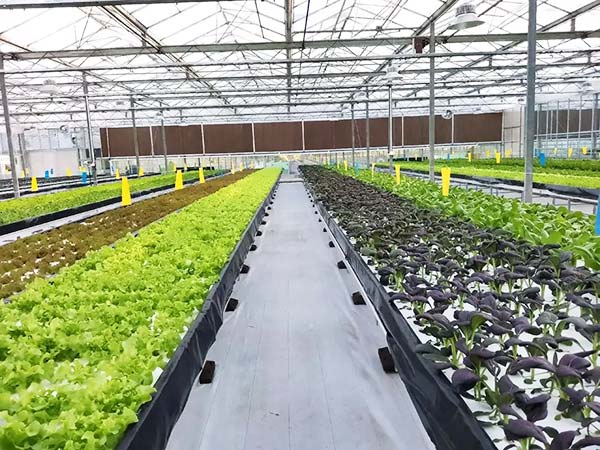

In commercial lettuce farming, the choice of equipment and its installation are equally important. Ventilation systems, irrigation systems, and heating equipment are essential. Lettuce thrives in temperatures between 15°C and 20°C, with ideal humidity levels between 50% and 70%. If labor costs are high in your area, automating with temperature and humidity sensors can greatly reduce the need for farm workers.
Read More: 9 Key Components of Automated Greenhouse Systems
2. Selecting Lettuce Seed Varieties
Whether you’re growing lettuce in a commercial or home greenhouse, choosing the right seeds is half the battle. High-yield and disease-resistant varieties are the best options. For example, ‘Butterhead’ and ‘Romaine’ are known for their resistance to diseases and excellent taste, making them suitable for most greenhouse growers. Apart from these, you also need to consider the adaptability of the varieties to ensure they thrive in your climate and greenhouse conditions. If you’re unsure about seed selection, the guide “Disease-Resistant Lettuce Varieties” can be a helpful resource.

3. Seedling Preparation
After choosing your seeds, the next step is seedling preparation, which is crucial for successful lettuce cultivation. This includes pre-germination, sowing, and managing young plants. Before planting, it’s recommended to treat the seeds and disinfect the soil. However, if you’re a hobbyist gardener, you can skip these steps. Generally, the best time to sow seeds in a greenhouse is when the temperature is stable between 15°C and 20°C, ensuring optimal germination.
Related Article: 12 Common Challenges in Greenhouse Seedling Management
Part 2: Grow Lettuce in a Greenhouse
1. Preparing the Growing Medium
Lettuce prefers slightly acidic soil with a pH of around 6.0. The soil should be loose, well-drained, and rich in organic matter. Common growing media formulas include a mix of sandy soil, peat, and organic fertilizers. If you’re using a soilless cultivation system, coconut coir or rock wool are good options. However, soilless cultivation requires precise nutrient management to ensure your lettuce gets all the nutrients it needs.

2. Transplanting the Seedlings
The day before transplanting, water the seedlings to ensure the soil is moist. This helps reduce root damage and allows the seedlings to adjust better to their new environment. When transplanting, dig shallow trenches about 4–6 cm deep and apply a mix of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers. After watering and waiting for the water to absorb, place the seedlings 20–30 cm apart and lightly cover the roots with soil. Be gentle during the entire process to avoid damaging the delicate root systems.

3. Managing Light
Ensuring adequate light is essential for lettuce to grow healthy and strong. If your lettuce receives insufficient light, the leaves may turn yellow, and the plants could become weak. Lettuce needs at least 10–12 hours of light per day. You may need to use artificial lighting to supplement natural sunlight, especially during darker seasons. The key is to adjust lighting based on the weather and seasons, ensuring consistent light exposure for your crops.

If you’re growing lettuce in a garden greenhouse, make sure it receives at least 6 hours of direct sunlight daily for optimal growth.
4. Managing Water and Nutrients
Proper water management is key to growing well-shaped and tasty lettuce. In greenhouses, drip and sprinkler irrigation are commonly used. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the roots, minimizing evaporation, while sprinkler irrigation covers a wider area and is suitable for larger-scale production. It’s recommended to mix liquid fertilizers with irrigation water for better growth results. Using organic fertilizers can also boost the growth of your lettuce.

For smaller gardens, a watering can is sufficient. The best time to water is early morning or late afternoon to reduce evaporation and ensure the roots absorb enough water. Lettuce has high nitrogen requirements and also needs phosphorus and potassium for root and leaf development.

During the seedling stage, use water-soluble organic fertilizers rich in humic acid. In the rosette stage, nitrogen and potassium requirements increase, but during the heading stage, reduce nitrogen and focus on potassium. If using organic fertilizers, ensure they are fully decomposed to avoid damaging the roots. Fertilization should be done in small amounts multiple times to prevent fertilizer burn.
5. Managing the Greenhouse Environment
After transplanting, maintain a temperature of 18°C to 22°C for the seedlings to establish. During the heading stage, keep the daytime temperature between 20°C and 22°C and the nighttime temperature between 12°C and 15°C. Managing humidity is also crucial. Relative humidity should be maintained between 50% and 70% to prevent disease.

A well-functioning ventilation system can help regulate airflow and reduce moisture retention, minimizing the risk of pests and diseases. By using temperature and humidity sensors with automated systems, you can continuously monitor and adjust the greenhouse environment, ensuring optimal conditions for lettuce growth.
6. Pest Control
Pest control is essential when growing lettuce in a greenhouse. You can use physical and biological methods, such as installing insect screens to keep pests out and using yellow sticky traps to catch flying insects. Regular ventilation can also help control humidity and inhibit pest growth. Proper crop rotation and soil management will also help reduce pest problems. If pests become a significant issue, consider organic pesticides or introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs or predatory mites to control pests naturally.
Don’t Miss: How to Keep Bugs Out of Your Greenhouse?
7. Pruning and Leaf Trimming
Pruning and leaf trimming are important tasks in greenhouse lettuce cultivation. It’s best to prune on sunny days using clean, sharp tools. Regularly trim old, diseased, or overcrowded leaves to improve air circulation and light penetration, which helps prevent pests and diseases. This also ensures that the nutrients focus on healthy leaves, improving the overall quality and yield of your lettuce.

Part 3: Harvesting
In lettuce cultivation, harvesting and post-harvest processing are crucial steps to ensure the quality of the final product. This section is particularly relevant for large commercial greenhouse growers, though understanding the best harvesting time can also benefit small garden enthusiasts.
1. Optimal Harvest Time
The best time to harvest lettuce is when the leaves have fully opened but have not yet aged. This ensures the best taste and nutritional value. Harvesting too early can result in overly tender leaves with less flavor, while harvesting too late may cause the leaves to become tough or bitter.

2. Harvesting Techniques
When harvesting, it’s recommended to use sharp tools to carefully cut the base of the lettuce. Avoid tearing or damaging the leaves, as keeping them intact helps extend their shelf life and reduces nutrient loss during processing. For varieties with dense leaf clusters, you can harvest the outer leaves first, leaving the inner leaves to mature further.

3. Storage and Transportation
After harvesting, lettuce should be washed, packaged, and transported as quickly as possible. When washing, use cold water to gently remove any soil or debris from the surface. Avoid soaking the lettuce for long periods, as this can cause excessive water absorption and affect the texture of the leaves.

When packaging, choose breathable materials such as perforated plastic bags to prevent moisture buildup and rot. During transportation, maintaining low temperatures and the proper humidity level can significantly extend the shelf life of the lettuce, ensuring it arrives at the market fresh and ready to sell, which will help you fetch a good price and maximize your profits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, whether you’re a small garden enthusiast or a commercial greenhouse farmer, growing lettuce in a greenhouse requires meticulous management. From choosing the right greenhouse, preparing seedlings, planting, to harvesting, each step plays a crucial role.
If you’re going to run a large greenhouse to grow lettuce, INSONGREEN’s commercial greenhouse and automated management systems will help you easily control the environment, maximize both yield and quality, and ensure your lettuce remains competitive in the market.
References:





