Just like we wear warm coats and scarves in winter, our greenhouses need similar protection against the cold. In high-latitude and high-altitude areas, where winters are typically colder, keeping the greenhouse warm is crucial. Cold temperatures can harm plant growth and flowering, affecting the quality and quantity of crops.
This article will cover the essentials of greenhouse heating and offer common methods for maintaining warmth, helping you prepare and protect your greenhouse as winter approaches.
Principle Behind Keeping a Greenhouse Warm in Winter
To maintain warmth in a greenhouse during winter, several steps should be followed to ensure the heat is used and kept effectively.
First, we need to reduce heat loss inside the greenhouse. Insulating materials like foam boards or double-layered plastic films can do this. These materials act like an extra layer of insulation, preventing the heat inside from escaping to the colder outside environment.
Besides preventing heat loss, it’s also important to capture, store, and generate heat effectively. For instance, during the day, opening shade cloths allow plants and soil inside the greenhouse to absorb heat. For those with a budget, solar energy collectors can be used. These systems collect sunlight during the day, convert it into heat, and then release it at night or during cold, cloudy weather to keep the greenhouse warm. Additionally, using geothermal energy or hot water circulation systems can also provide a stable source of heat for the greenhouse.
16 Tips to Keep Your Greenhouse Warm in Winter
After understanding the basic principles of greenhouse warming, it’s time to delve into specific practical tips and suggestions. These tips are designed to help you manage your greenhouse environment more effectively, whether you’re on a limited budget or able to invest in more advanced technology. Here, we present 16 practical tips to help keep your greenhouse warm and your plants growing in winter.
For Small Greenhouses (Home Level)
For small, home-use greenhouses, simple and cost-effective methods are more suitable, such as:
1. Insulation Blankets or Curtains
Using insulation blankets or thick curtains to cover the greenhouse on cold nights can significantly reduce heat loss. This method is simple, cost-effective, and especially suitable for sudden cold weather. You can buy specialized greenhouse insulation materials at local garden stores or online, or you can use thick fabric from home as your greenhouse’s insulation blanket.
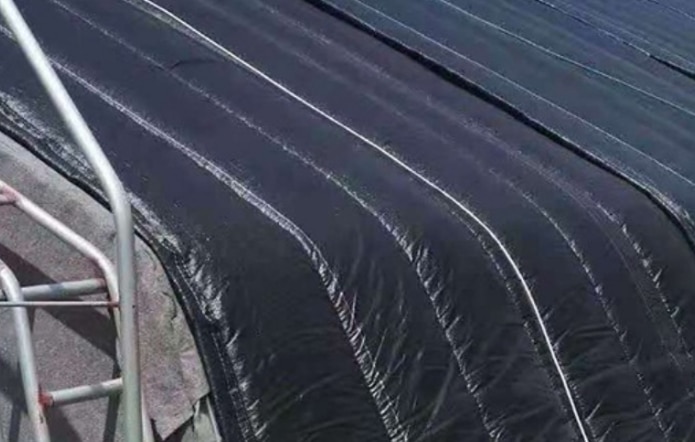

When choosing, opt for materials that are lightweight yet provide good insulation and allow light penetration. Then, install hooks or brackets on the greenhouse frame and secure the insulation material on top, making sure it covers the top and sides of the greenhouse.
Note: Remember to open the insulation blankets during the day when temperatures rise, and sunlight is available to allow the greenhouse to absorb sunlight. Alternatively, consider adding lighting inside the greenhouse to enable plants to perform photosynthesis.
2. Windbreaks
Strategically planting trees or setting up windbreak structures around the greenhouse is a practical and aesthetically pleasing way to reduce the invasion of cold winds. This not only helps to increase the internal temperature of the greenhouse but also adds natural beauty to your garden.
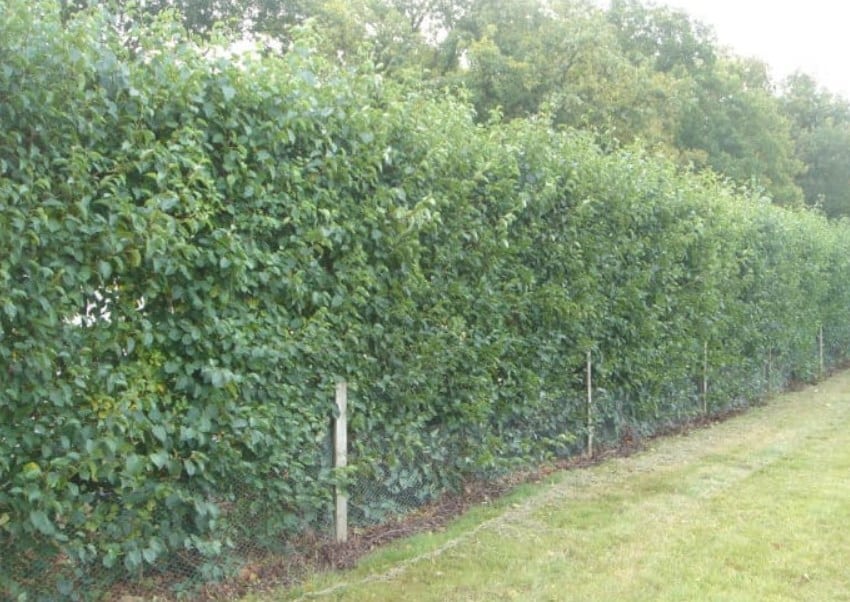

Choose tree species or shrubs that are cold-resistant and suitable for the local climate. They will not only provide extra protection for the greenhouse in winter but also enrich the biodiversity of your garden. Consider the growth habits and height of the plants to maximize the windbreak effect while avoiding blocking sunlight, ensuring sufficient light for the greenhouse plants.
3. Simple Insulation Materials
Foam plastic boards are a lightweight and economical insulation option, perfect for small greenhouses. They can be easily attached to the greenhouse’s inner walls, effectively maintaining the internal temperature and improving warmth in winter. Although these boards might slightly reduce light transmission, their insulation benefits in cold seasons are significant.
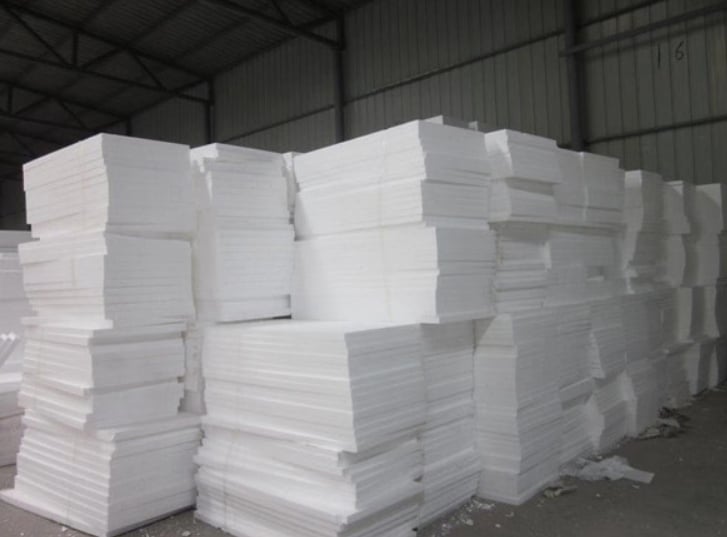

For small or mini-greenhouses, you can easily remove the foam boards as needed, such as taking them down during sunny days to let plants and soil absorb heat and reinstalling them at night to keep warm. However, larger commercial greenhouses may need to consider more professional insulation solutions.
4. Soil Heat Storage
Soil heat storage is a strategy that uses soil as a natural heat source, particularly suitable for small greenhouses. The core of this method is to use the natural ability of soil to absorb and store heat during the day. During the day, sunlight directly heats the soil, raising its temperature and storing heat.

At night, when the air temperature inside the greenhouse drops, this heat stored in the soil is gradually released, helping to maintain a warm environment inside the greenhouse.
There are some steps to implement soil heat storage
- Choose the right soil: Select soil types that can effectively absorb and store heat, such as soil rich in organic matter and clay.
- Increase soil depth: Increase the thickness of the soil layer inside the greenhouse to enhance its heat storage capacity.
- Maximize sunlight reception: Ensure the greenhouse can receive ample sunlight, allowing the soil to absorb as much heat as possible during the day.
- Nighttime covering: Cover the soil surface with materials like straw mats or insulation fabric at night or in cold weather to reduce heat loss.
- Adjust covering as needed: Remove or cover the soil as per the weather conditions to balance heat absorption and retention.
5. Ordinary Plastic Film
For garden enthusiasts with a limited budget, covering the greenhouse with ordinary plastic film is an economical and practical choice. This single-layer transparent film may not insulate as well as double-layered film, but it’s more cost-effective and easier to install.
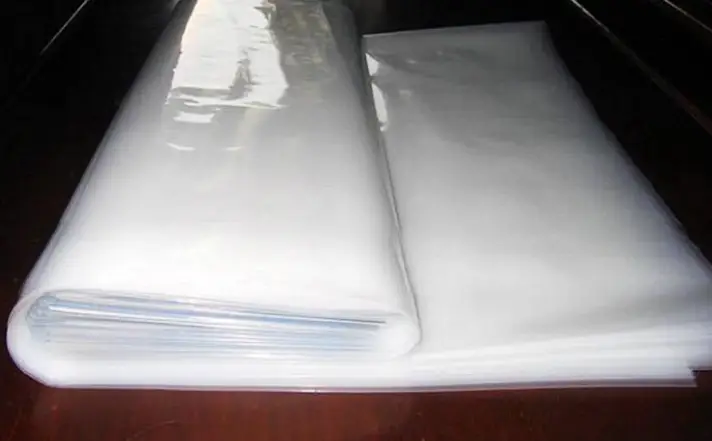

It provides basic insulation, sufficient for milder winter climates. This type of film, found in most garden supply stores, is easy to set up and perfect for beginners or small-scale greenhouse applications.
6. Greenhouse-Livestock Integrated System
The Greenhouse-Livestock Integrated System is an innovative method that combines a small greenhouse with livestock farming. This system effectively uses the heat generated by the animals to naturally warm the greenhouse. It utilizes the heat from the livestock’s body temperature, breathing, and the fermentation process of their manure. Additionally, the heat produced during the composting of animal manure can be transferred to the greenhouse, further increasing the temperature.

This method not only improves energy efficiency but also reduces environmental pollution by recycling farm waste. However, it’s essential to ensure the welfare and health of the animals and consider proper isolation measures to prevent potential disease transmission.
For Medium and Large Greenhouses
Medium and large greenhouses, with their larger spaces and structures, require special warming strategies to ensure even temperature distribution and healthy plant growth. Due to their scale and operational complexity, the insulation materials and techniques used are more advanced and professional, especially in large commercial greenhouses.
Here are some warming tips suitable for medium and large greenhouses:
7. Thermal Curtain System
The thermal curtain system, combined with climate screens, offers an efficient energy-saving and temperature-control solution for modern greenhouses. At night, this system unfolds special insulation curtains to significantly reduce heat loss through the greenhouse’s top and sides, lowering energy consumption while keeping the interior warm.

Climate screen technology further enhances the system’s effectiveness by precisely controlling greenhouse conditions, including light, temperature, and humidity. These adjustable curtains and screens can be opened or closed flexibly depending on different climate conditions, providing the most suitable growing environment for plants and optimizing energy use.
Recommended Products: 6 Different Types of Climate Screens for Commercial Greenhouses
8. Double-Layered Plastic Film
Double-layered plastic film is an effective insulation solution for medium-sized greenhouses. Its key feature is an air layer between two plastic layers, similar to double-glazed windows. This air layer enhances insulation, effectively retaining heat inside the greenhouse while allowing enough light for photosynthesis.

This cost-effective option is ideal for medium-sized greenhouses seeking a balance between insulation and affordability. Although installation requires some skill and precision, the long-term energy-saving benefits and ability to maintain a constant temperature make it a worthwhile investment for greenhouse operators.
9. Multi-Functional Covering Materials
Multi-functional covering materials, such as adjustable light shading nets or films with variable light transmission, allow gardeners to precisely control the light intensity and temperature inside the greenhouse according to different seasons and plant needs. Popular choices include Polyethylene Film and Polycarbonate Sheets.
Polyethylene film is economical, while polycarbonate sheets offer better durability and insulation. These covering materials provide essential insulation and help maintain suitable light levels.
10. Top-Efficient Insulation Materials
Top insulation is crucial for large greenhouses. Highly efficient insulating materials, such as double-glazed glass or special insulated roofing panels, can effectively reduce heat loss from the top. These materials have high insulation performance while ensuring enough natural light enters the greenhouse. Double-glazed glass provides superior insulation, and reflective coatings or green roofs are innovative options for adding an extra layer of insulation.
11. Hot Air Blower System
The hot air blower system is designed for large greenhouses, offering a quick and efficient way to heat. Its main advantage is the rapid response to temperature changes, quickly warming the space by blowing heated air. This system is particularly useful in extremely cold climates or situations where rapid temperature adjustments are needed in the greenhouse.

12. Passive Solar Design
Passive solar design is a method of building greenhouses that focuses on using natural light and heat to reduce the need for artificial heating. By adding south-facing windows and using high-efficiency materials like double-glazed glass, polycarbonate panels, or double-layer film, this design greatly improves the greenhouse’s ability to capture and retain heat. This makes the greenhouse more eco-friendly and cost-effective.
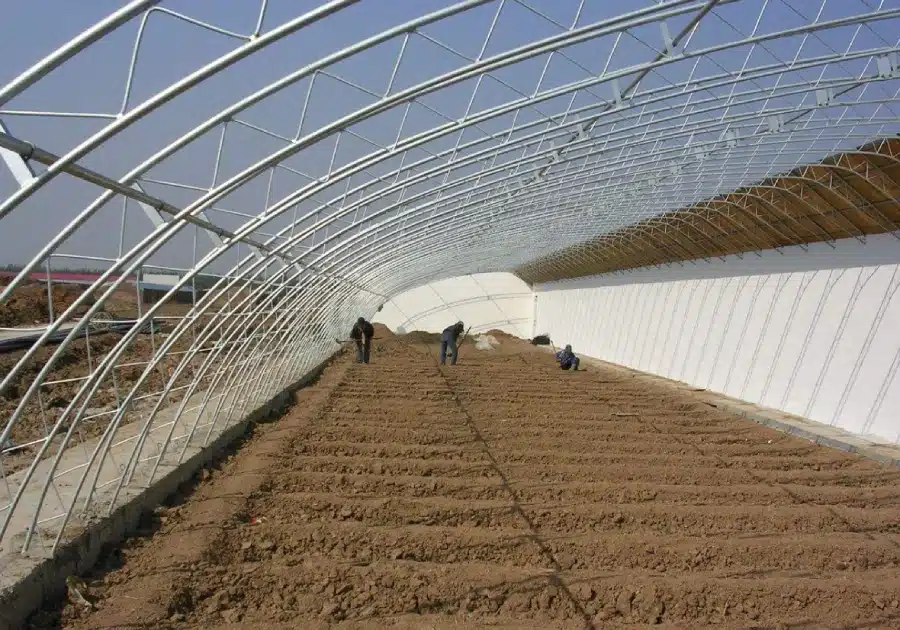

Chinese passive solar greenhouses are a great example of this design. They have three solid walls made of bricks or clay, with the fourth wall facing south and covered in transparent plastic film to maximize sunlight absorption. During the day, the south-facing wall captures solar energy, while the thick walls store heat. At night, this stored heat is slowly released to keep the greenhouse warm. Additionally, using insulation curtains at night helps reduce heat loss even further.
This type of greenhouse can keep the inside temperature up to 25°C (45°F) warmer than outside during winter, all by using solar energy. This not only saves energy but also reduces operating costs, making it an efficient and sustainable solution for agriculture.
13. Heat Recovery System
The Heat Recovery System is an innovative technology that captures and recycles heat from the air inside the greenhouse. It utilizes excess heat, for instance, generated by the exhaust system, and recirculates it back into the greenhouse.
This reduces reliance on external heat sources and significantly lowers energy consumption, making it crucial for efficient energy management and cost reduction, especially in larger commercial greenhouses.
14. Smart Control System
With advanced sensors and control technologies, the Smart Control System automatically adjusts the temperature, humidity, and light levels inside the greenhouse. It precisely controls the environment based on real-time data and preset parameters, ensuring optimal growing conditions.
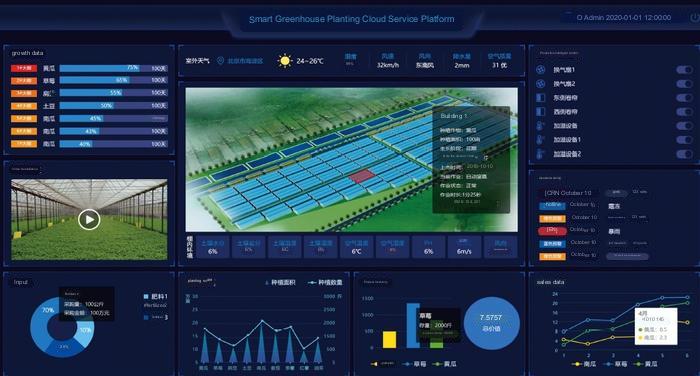
The system not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances crop growth quality and yield. It’s an ideal choice for large greenhouse operators seeking high-precision environmental control and increased crop production.
15. Solar Collectors
Solar collectors, which use solar energy to provide heat for the greenhouse, are a sustainable and eco-friendly warming method. Installing solar panels to collect solar energy and release heat as needed, these systems are particularly suitable for medium to large greenhouses in sunny areas. Though the initial investment might be high, solar collectors significantly reduce long-term energy costs and support sustainable greenhouse operations.

16. Geothermal Heating System
If your greenhouse is located in an area rich in geothermal resources, utilizing natural geothermal energy for heating is an excellent option. This system captures heat from underground and efficiently transfers it to the greenhouse through a series of pipes.
Compared to traditional heating methods, geothermal heating provides a more consistent and reliable temperature control, ensuring uniform and stable temperatures inside the greenhouse, and is environmentally friendly.
FAQ:
1. How to Keep A Greenhouse Warm without Electricity?
Keeping a greenhouse warm without electricity involves natural and passive methods. For example, it is key to make the most of solar energy by ensuring the greenhouse receives as much sunlight as possible during the day. At night or on cloudy days, covering the greenhouse with foam boards or insulation blankets helps to reduce heat loss.
Additionally, using the heat generated by composting or placing bottles or buckets of hot water in the greenhouse can release heat at night. Setting up windbreaks and shelters around the greenhouse reduces the impact of cold winds, and using geothermal energy or soil heat storage can provide heat.
2. The Cheapest Way or Even Free Way to Heat A Greenhouse in Winter?
The most economical or even free way to heat a greenhouse in winter is to maximize the use of natural resources. During the day, opening shade cloths or other coverings can capture as much sunlight as possible. At night or in cold weather, use foam plastic, insulation blankets, and other materials we mentioned above to retain heat in the greenhouse.
Additionally, the heat from composting or the heat generated by your livestock can provide extra warmth for the greenhouse. In windy areas, setting up windbreaks can reduce heat loss from the greenhouse.
3. Is There Any Small Greenhouse Heating Systems?
There are various heating system options for small greenhouses, including small electric heaters, hot air blowers, and solar heaters. Small electric heaters are easy to install and use but require a power source. For greenhouses without electricity, consider using propane or natural gas heaters, keeping ventilation and safety in mind.
Solar heaters are an eco-friendly option, especially suitable for areas with plenty of sunlight. Solar panels collect energy and convert it into heat for your greenhouse. Lastly, most of the methods mentioned in this article can be tried, depending mainly on your budget.
4. What is Deep Winter Greenhouse?
A deep winter greenhouse is designed to maintain plant growth during the cold winter months. It focuses on using passive solar heating and effective insulation designs to maximize the use of natural light and maintain indoor temperatures. These greenhouses are typically built facing south to capture more sunlight and use efficient insulation materials to reduce heat loss.
They are often equipped with heat storage systems, like using large amounts of soil, water buckets, or stones to store heat during the day and release it at night, keeping the greenhouse warm. Deep winter greenhouses are ideal for year-round planting in cold regions, especially for those pursuing sustainable agriculture and energy-saving lifestyles.
Conclusion
In summary, keeping your greenhouse warm in winter is essential, no matter its size or your climate challenges. We’ve shared a variety of warming tips and strategies, ranging from simple to advanced, to help you protect your plants and ensure your greenhouse runs efficiently.
If you’re planning to build a commercial greenhouse, our team is here to help. We offer tailored greenhouse design, production, and construction services for clients around the world. Whether you have specific needs or unique environmental conditions, don’t hesitate to contact us. Let’s work together to create the perfect greenhouse for you.





