Are you thinking about building a large glass greenhouse for agricultural production? Do you want to know the costs of commercial glass greenhouses?

You’re in the right place. Following our previous article, which discussed 12 key factors to consider before constructing a commercial glass greenhouse, this article will delve deeper into the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs of commercial glass greenhouses, as well as discuss their potential profits and returns.
Initial Investment for Commercial Glass Greenhouses
The construction cost of a basic commercial glass greenhouse includes several components, such as civil engineering, framework, and covering materials. For example, in China, a commercial glass greenhouse that is 6 meters tall and covers 10,000 square feet typically costs between $125,000 and $186,000 to equip with basic systems. In the U.S., the cost can range from $200,000 to $300,000.
Of course, if you opt for more advanced systems, like lighting, environmental control, or intelligent control systems, the total cost will increase based on your needs, potentially exceeding $400,000.
1. Civil Engineering
The civil engineering aspect of greenhouses includes foundational work, ground treatments, drainage, and electrical systems, generally making up 20%-30% of the total cost. Labor costs vary by location. In China, these expenses are about $1.00-$1.30 per square foot. In the U.S., they range from $2-$6 per square foot.

2. Steel Framework
The greenhouse’s steel framework provides structural support and includes columns, beams, arches, and connectors, accounting for 15%-20% of overall costs. Steel prices can fluctuate, so here’s an estimated cost range for reference. In China, the total cost for the primary structure of a glass greenhouse is around $1.26-$1.79 per square foot, whereas in the U.S., it ranges from $2.50-$3.60 per square foot.

3. Covering Materials
Greenhouses covering options vary based on individual needs or geographic location, including tempered or non-tempered glass and single or double glazing. Additionally, aluminum profiles are necessary to secure the glass. This cost generally accounts for 20%-30% of the total.
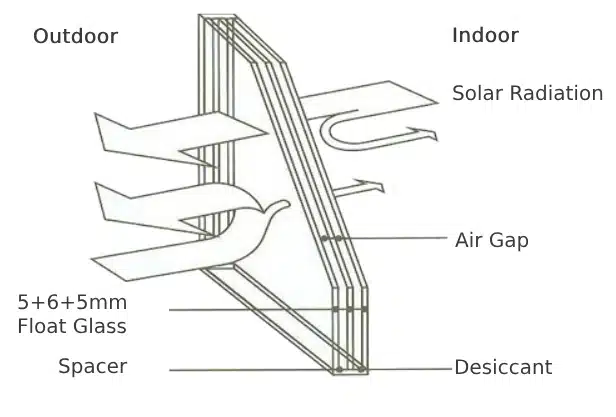
The performance and price of different glass types and external aluminum profiles vary. For instance, the cost for glass covering materials in China is about $0.64-$0.97 per square foot, while in the U.S., it reaches approximately $2.50 per square foot.
4. Shading Systems
Shading systems consist of external and internal parts. The external shading system includes a drive system and a black round-pin net with a 75% shading rate, whereas the internal system uses a drive system and an aluminum foil shading net. Internal shades reflect solar heat, helping cool the greenhouse interior.

This component represents 10%-15% of the total cost. In China, the system costs about $0.33 per square foot; in the U.S., the cost ranges from $1.00 to $1.50 per square foot.
5. Cooling Systems
Cooling systems are crucial in commercial glass greenhouses, featuring wet walls, fans (like the commonly used 1380 model in China), sprinkler systems, and motorized vent windows. These elements make up 15%-20% of the total cost. In China, the cost is approximately $0.21 per square foot. In the U.S., more advanced climate control systems are standard, costing around $2.00 per square foot.

6. Greenhouse Ventilation Systems
Ventilation systems maintain air circulation within the greenhouse through roof vents, side windows, and exhaust facilities, accounting for 10%-15% of the total cost. In China, this cost is around $0.39 per square foot. Conversely, in the U.S., more advanced commercial greenhouse ventilation systems typically cost about $2.50 per square foot, with the average price of an exhaust fan at about $125.

7. Installation and Transportation
Once greenhouse materials are ready, they need to be transported to a designated location for installation, incurring transportation and installation costs. These expenses can vary significantly, accounting for 5%-20% of the total cost. Factors influencing these costs include the region, the amount and distribution of greenhouse materials, and geographic location.
Operating and Maintenance Costs of Glass Greenhouse
After your glass greenhouse is constructed, the next costs to consider are those for operation and maintenance. These ongoing expenses are crucial for the long-term success and sustainability of the greenhouse. While specific figures can’t be given here, we can discuss four main factors that impact these costs, allowing you to make a rough estimate of future expenses for your greenhouse farming.
1. Daily Energy Consumption (Heating, Cooling, Lighting)
Commercial glass greenhouses, especially smart ones, incur fixed monthly energy costs, primarily from the following systems:
- Heating: In cold regions or seasons, heating is one of the major energy expenses. Common methods include using natural gas, electric heating, or biomass fuels. Energy costs vary based on the region, type of energy used, and the greenhouse’s insulation performance. Maximizing the use of the cheapest local energy sources for heating can be cost-effective.
- Cooling: In hot climates, effective ventilation and cooling systems are essential for maintaining suitable greenhouse temperatures. Potential cooling systems include wet-wall fan systems, shade curtains, and water circulation cooling systems. Combining natural and forced ventilation can effectively reduce energy consumption while keeping the greenhouse temperature close to the external temperature.
- Lighting: In greenhouse management, lighting is not only a basic necessity but also a critical tool for adjusting and optimizing the growth cycles of crops. Using supplemental lighting, especially LED lights, can effectively extend the growing season and increase yield, particularly in seasons with insufficient natural sunlight.

2. Water Resource Management
Commercial glass greenhouses often use drip or spray irrigation systems to efficiently manage water resources. If operating in arid regions like the Middle East, further reducing water wastage and lowering water costs are critical through the recycling of rainwater and irrigation water.

Moreover, the quality of water in greenhouses impacts crop growth. Ensuring irrigation water quality may require additional costs for daily filtering, disinfection, and testing.
3. Regular Maintenance and Repair
Regular inspections and maintenance of greenhouse structures (like cleaning glass, replacing broken panes, and checking and repairing ventilation windows) and systems (such as irrigation, heating, and cooling systems) are essential for long-term operation and minimizing breakdowns. Even with the best maintenance, greenhouse equipment and structures may occasionally need repairs. Budgets should include costs for equipment replacement and repairs.
4. Labor Costs
The management team handles daily operational decisions, financial management, marketing, and sales. Managerial salaries are a part of greenhouse costs. Operational staff are responsible for planting, pruning, harvesting, packaging, and maintenance tasks. Their salaries and any necessary training expenses should be included in operational costs.
These operating and maintenance costs require careful planning and management to ensure economic efficiency. For instance, investing in energy-saving technology, optimizing irrigation and fertilization plans, regularly maintaining equipment and structures, and training staff to improve efficiency can significantly reduce these costs.
Glass Greenhouse Profits and Returns
Commercial glass greenhouses provide a controlled environment that ensures the year-round production of high-quality crops, even during off-season periods, allowing for higher market prices and increased profits. Beyond direct sales, commercial greenhouses can also generate additional income through educational tours, consultancy services, and research services.

Although the initial investment costs are relatively high, adopting energy-efficient technologies, water resource management, and smart management software can offset these costs, lowering operational expenses and enhancing efficiency.
Conclusion
From the analysis above, it’s clear that starting a commercial glass greenhouse project requires careful consideration of many factors and a substantial initial investment. Additionally, ongoing operations and maintenance also demand significant ongoing financial input.
However, given the strong market demand for high-quality fresh fruits and vegetables, such an investment undoubtedly signifies long-term profit potential. Thus, despite various challenges, investing in a commercial glass greenhouse remains a highly attractive option.
As a company specializing in commercial greenhouse construction, INGONGREEN is always open to your inquiries and looks forward to exploring the boundless possibilities of greenhouse construction with you.





