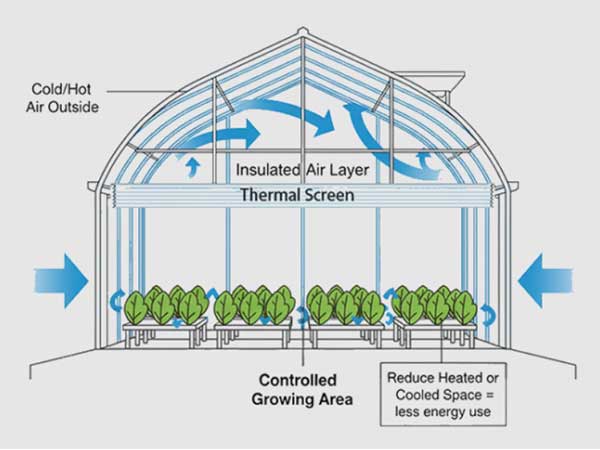
As the saying goes, “light is the life of plants.” In a greenhouse, lighting is critical to plant growth and crop yield. Good lighting not only helps plants produce more energy through photosynthesis but also improves plant quality and reduces pests and diseases.
In this article, we will provide 8 tips for optimal greenhouse lighting to maximize crop growth.
Why is Lighting Important for Greenhouse Plants?
Plants rely on sunlight to produce energy through photosynthesis, which is essential for plant growth and development. However, not all light is created equal. In a greenhouse, plants receive artificial light in addition to natural sunlight.
The quality and quantity of light can directly affect plant growth, development, and yield. Insufficient light can cause stunted growth, delayed flowering, and poor fruit quality. Excessive light can also be harmful, causing leaf burn and reducing photosynthetic efficiency. Therefore, it is important to provide the right amount and quality of light to plants in a greenhouse.
8 Tips for Optimal Greenhouse Lighting
Tip 1: Proper Plant Selection
When planting different types of vegetables in a greenhouse, it is important to plant them according to the “north high and south low” principle. The seeds should be sown in one direction, and the seedlings should be transplanted with their cotyledons parallel to each other. Strict cultivation specifications should be followed to promote even plant growth and minimize shading between plants. For larger greenhouses with good conditions, tall and short vegetables can be mixed and grown together.
Tip 2: Use Dripless Film
Most plastic films sold on the market are ordinary films. In a greenhouse, the high humidity often causes water droplets to condense on the film, which can block sunlight and reduce its transparency. Therefore, it is recommended to use dripless film to prevent this problem.
Tip 3: Keep the Film Clean
The external walls of the greenhouse should be cleaned regularly to remove dust and dirt. In snowy weather, the snow on the greenhouse should be promptly cleared to increase the transparency of the film.
Tip 4: Double-layer Insulation
By adding a ground cover or a ground arch to the greenhouse, the ground temperature can be increased by 2°C, according to experiments. Small arches can also be set up to maintain a temperature of over 10°C. This helps to promote the normal growth and development of vegetables in the winter.
Tip 5: Use an Anti-cold Trench
By covering the perimeter of the greenhouse with straw and digging an anti-cold trench, with a width of about 30cm and a depth of about 50cm, filled with materials such as rice straw and rice husks, the greenhouse can be separated from the cold air, which can increase the temperature inside. In addition, laying horse manure and organic fertilizers in the greenhouse can also increase soil and near-surface air temperatures.
Tip 6: Remove Anti-cold Materials Timely
On sunny mornings, the anti-cold materials should be removed when the sunlight shines into the greenhouse and removed later in the day on cloudy or snowy days. The materials should also be rolled up tightly to expand the light exposure area and increase the indoor temperature.
Tip 7: Use Supplemental Lighting
In cloudy or snowy weather, when the intensity and duration of natural light are insufficient, supplemental lighting can be used to increase the photosynthetic efficiency of vegetables. Artificial light sources such as electric lamps, gas lamps, or biogas lamps can be used as needed.
Tip 8: Install Windbreaks
By using a straw to make 1-2 layers of windbreaks on the upwind side of the greenhouse, heat loss can be minimized and the internal temperature of the greenhouse can be better maintained. This is especially important in areas with strong winds and low temperatures. In addition, windbreaks can also reduce damage to crops caused by strong winds.
Conclusion
In summary, optimal greenhouse lighting is essential for maximizing crop growth and yield. By following these 8 tips, greenhouse owners can ensure that their plants receive the right amount and quality of light, while also taking steps to maintain optimal growing conditions.