Roses are often symbols of romance and popular gifts for loved ones and friends. Beyond this, they have extensive applications in various industries like food, perfume, cosmetics, and medicine. According to the Cut Flowers – Global Strategic Business Report, the rose market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2%, reaching $15.8 billion by the end of the forecast period. This growth indicates a rising demand for roses in the market.

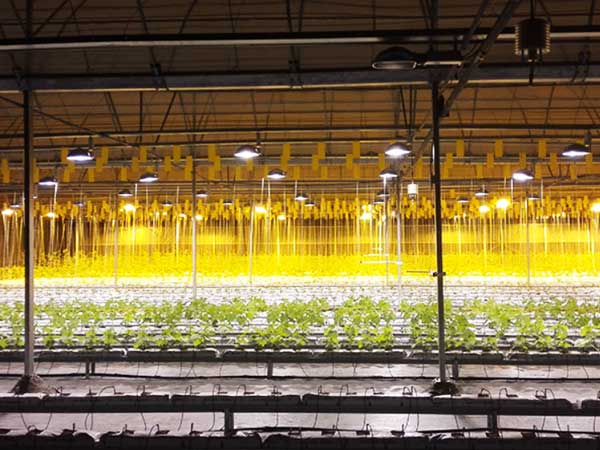
Roses are very sensitive to their growing environment. Small temperature, humidity, and light changes can significantly affect their yield and quality. Greenhouse technology can provide an ideal growing environment for the mass cultivation of roses, helping to improve both yield and quality despite natural challenges.
This article will explore key factors to consider when growing roses in a greenhouse. We will also offer practical tips to help you stay competitive.
Section 1: Choosing the Right Greenhouse for Rose Cultivation
There are many types of greenhouses, and the costs can vary significantly depending on the materials used and the smart systems included.
1. How to Choose the Right Greenhouse?
If your rose garden is in tropical or subtropical regions, economical poly tunnels may suffice. However, in temperate or higher latitude areas, you might need to choose more expensive glass or polycarbonate greenhouses. These options provide better insulation and durability during winter.
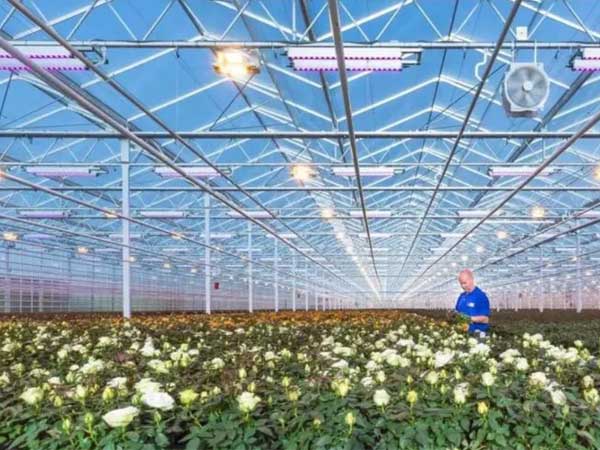

If you are a gardening enthusiast focused on cost control, a simple plastic tunnel, which is relatively cheaper, would typically suffice. For large-scale commercial rose cultivation, especially if you focus on high-end varieties, investing in a smart greenhouse might be necessary.
Don’t Miss: 10 Advantages of A Commercial Smart Greenhouse
2. Costs of Greenhouses for Rose Cultivation
Home-Scale Small Greenhouses
For small poly greenhouses without complex systems, the price is quite affordable. You can purchase ready-made ones from local agricultural stores or online shops and assemble them quickly following instructions. On Amazon, portable greenhouses are priced under $100. Of course, greenhouse prices can vary widely across different regions.
If you are handy, you can buy raw materials and follow some DIY tutorials to build your own greenhouse.
Large-Scale Rose Cultivation
The initial construction costs can be quite high for commercial greenhouses that support large-scale rose cultivation. For example, even the cheapest polytunnels measuring 8 meters by 30 meters (25 feet by 100 feet) cost about $12,000 in Nigeria.
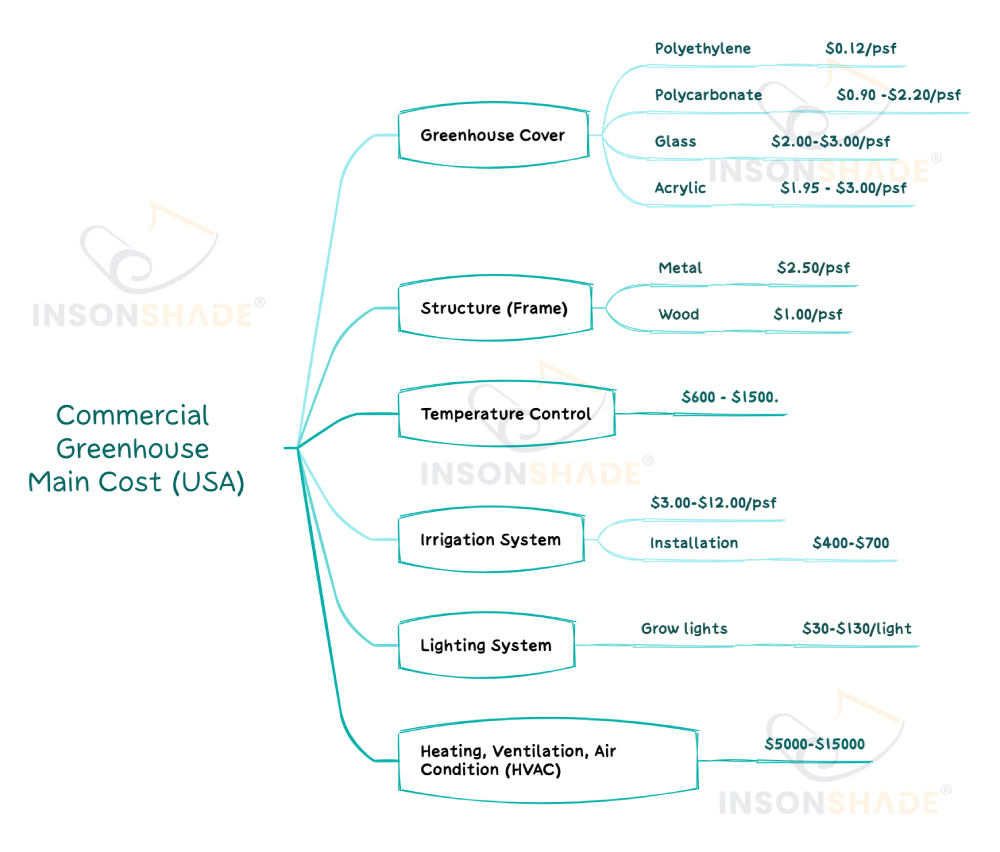
The costs will be higher if you are considering modern greenhouses with climate control systems. For example, a 100ft by 100ft commercial greenhouse in the United States can cost between $200,000 and $300,000.
3. Yield of Greenhouse-Grown Roses
From optimizing growing conditions to improving harvesting efficiency, greenhouse technology significantly enhances the yield and quality of roses. Whether using low-cost plastic film greenhouses or high-end glass or polycarbonate smart greenhouses, the yield and quality are superior to naturally grown roses.
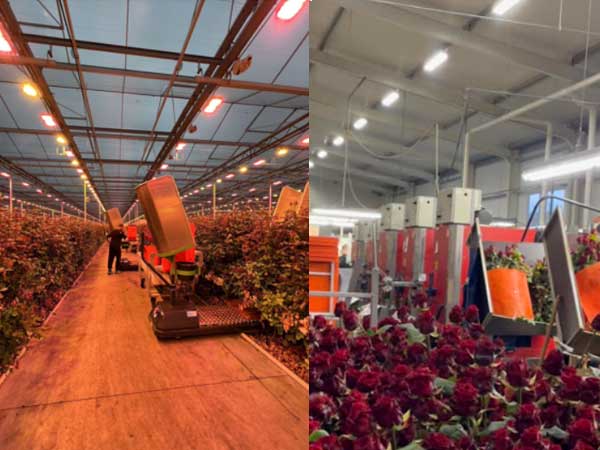

By integrating sensor networks, data analysis tools, and automated monitoring systems, rose production in greenhouses can be highly automated. Some greenhouse rose producers operate efficiently 24/7, with automated production lines processing 10,000 roses per hour. The annual yield can exceed 300 high-quality roses per square meter.
Section 2: Growing Conditions for Greenhouse Roses
Ensuring optimal soil pH, light, temperature, and moisture management is crucial when growing roses in a greenhouse. These factors directly impact the roses’ health, growth rate, quality, and yield.
1. Soil Requirements
Roses thrive in soil with a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. They prefer loose, fertile, and well-drained soil. Roses also need trace elements such as iron, zinc, and manganese, which are important for their growth and flowering. After harvesting cut flowers, apply well-rotted organic fertilizer around the plants and water thoroughly in winter.
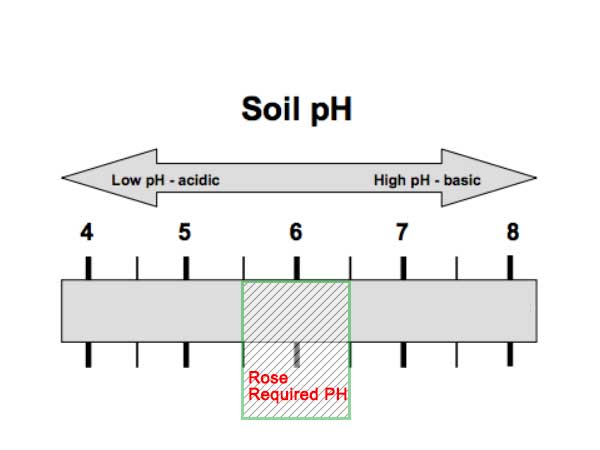
If you use a smart greenhouse for soilless cultivation, you do not need to worry about these soil conditions.
2. Light
Roses are like sun-loving dancers; their growth and flowering depend on sunlight. They need at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight daily to stay vibrant and lively. Did you know many large rose plantations are in high-altitude areas like Yunnan in China, Ethiopia in Africa, and Ecuador in South America? These regions, situated above 2000 meters, receive more intense sunlight, making the roses’ colors more vibrant. This light requirement also includes artificial lighting when necessary.
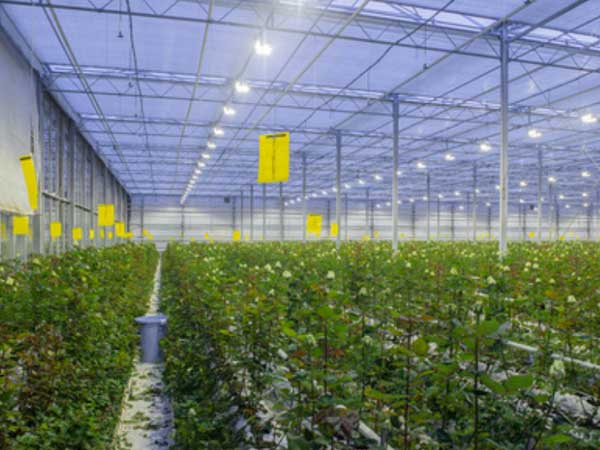

3. Temperature
Temperature is also crucial. It greatly affects the size of the rose flowers. The optimal daytime temperature for rose growth is between 22 and 27 degrees Celsius, and the night temperature should be maintained between 15 and 18 degrees Celsius.

Remember two important points about daily temperature transitions: the transition from night to day and from day to night. The intensity and duration of these transitions significantly affect plant growth. A rapid temperature increase from night to day often weakens the leaves’ photosynthetic activity, making the flower buds thin and weak. The transition from night to day should last at least two hours.
4. Humidity Conditions
The relative humidity in your greenhouse is also an important parameter. A relative humidity of 70-85% supports active growth, providing optimal conditions for photosynthesis. When the humidity exceeds 90%, the risk of powdery mildew increases. Conversely, if the relative humidity falls below 50%, the risk of spider mites and powdery mildew rises, leading to a sharp decline in the quality of your roses and affecting their market price.
5. Water Management
Drip irrigation is primarily used for watering greenhouse roses. Roses are drought-tolerant but do not thrive in overly wet conditions. The watering principle should be “water thoroughly when dry.” Morning is the best time to water. If you notice no dew on the edges of the rose leaves in the morning, it means the soil in your rose garden is dry, and you should water immediately.

6. Carbon Dioxide Levels
Low carbon dioxide levels in greenhouses can limit the photosynthesis required for high yields. Carbon dioxide consumption is crucial for plant growth. When the concentration of carbon dioxide in the greenhouse air increases from 300 ppm to 900 ppm, the intensity of photosynthesis and productivity can increase by 50%.
Section 3: Greenhouse Rose Propagation
In greenhouse cultivation, roses are primarily propagated through two asexual methods: grafting and cuttings. Plants from cuttings can be harvested for 4 to 5 years after planting, while those from grafting can be harvested for 6 to 7 years, with multiple crops produced each year. Below, we briefly describe these two propagation methods for your reference.
Grafting
Grafting is one of the most common methods for propagating roses. Follow these steps for successful grafting:
- Select several healthy branches from a strong plant.
- Keep the scion (the grafted part) clean to avoid contamination.
- Align the scion with the rootstock.
- Secure the graft with wire and cover it with a plastic bag, leaving a small opening.
- Maintain appropriate temperature and moisture levels.
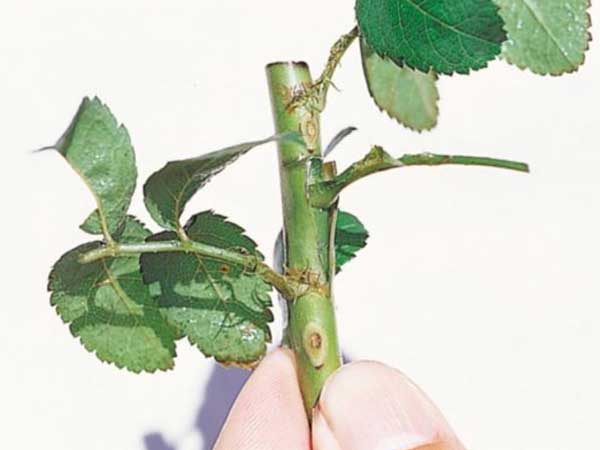

Successful union of scion and rootstock in grafted roses.
Cuttings
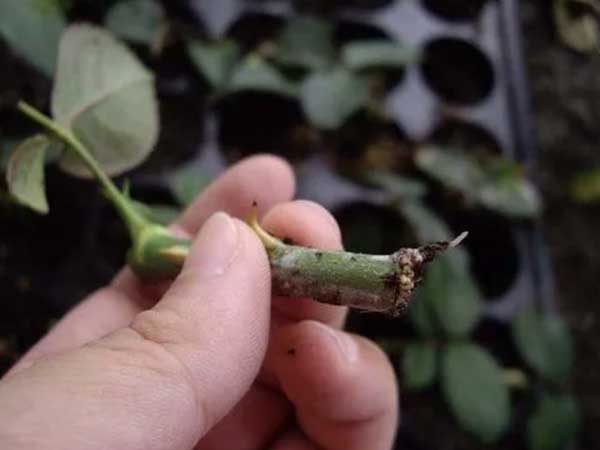
Cuttings involve using healthy branches to grow new plants. Here’s how to do it:
- Select healthy branches free from pests and diseases.
- Cut the branches into 3 to 4 segments, keeping the top bud section.
- Retain 2 to 3 leaves in the middle section.
- Disinfect the cut ends with a potassium permanganate solution.
- Insert the cuttings into nutrient bags at a depth of about 4 to 6 cm.
- Water adequately.
In about a month, the cuttings will develop roots and start to sprout.

Section 4: Disease and Pest Management
When growing roses in a greenhouse, the most common diseases include black spot, powdery mildew, and botrytis blight. The main pests are red spider mites, leaf mites, and thrips. Here, we provide some methods for managing diseases and pests in greenhouse roses, which we hope will be helpful to you.
1. Common Diseases
- Black Spot: This fungal disease causes black spots on leaves, leading to leaf drop. To prevent it, maintain good air circulation, avoid overhead watering, and use fungicides as needed.
- Powdery Mildew: This disease appears as white powder on leaves and stems. It thrives in high humidity. Control it by reducing humidity, ensuring good air circulation, and applying appropriate fungicides.
- Botrytis Blight: This disease causes grey mold on flowers and leaves. It is prevalent in cool, moist conditions. Prevent it by removing infected plant parts, improving air circulation, and using fungicides.
2. Common Pests
- Red Spider Mites: These tiny pests suck sap from leaves, causing them to turn yellow and drop. Control them by maintaining high humidity, using insecticidal soaps, and introducing natural predators like ladybugs.
- Leaf Mites: These pests cause leaves to curl and become distorted. Manage them with miticides and by encouraging beneficial insects.
- Thrips: These small insects damage flowers and leaves by sucking their juices. Control them with insecticidal soaps, sticky traps, and introducing natural predators.
3. Resources for Further Reading
- Rose Diseases (Greenhouse): Detailed information on managing rose diseases in greenhouses can be found on the PennState Extension website.
- IPM Program Successful in California Greenhouse Cut Roses: Learn about successful integrated pest management (IPM) programs from the University of California, Agriculture and Natural Resources.
- How to Keep Bugs Out of Greenhouse? Get 20 Methods: Discover effective methods for keeping bugs out of your greenhouse here.
Section 5: Greenhouse Roses Caring
Pruning is a crucial part of managing rose production. There are two types of pruning: blooming season pruning and dormant season pruning.
1. Blooming Season Pruning
During the blooming season, pruning should be combined with flower harvesting. After the first batch of flowers blooms, trim the stems back to 10-15 cm above the base. This promotes the growth of more and better-quality flowers in the next bloom.
2. Dormant Season Pruning
Dormant season pruning is done in early spring before new growth starts. For each plant, retain 4-5 main stems, trimming them to 40-50 cm above the ground. Each main stem should have 1-2 side branches, with each side branch pruned to leave two buds. Remove any dead or diseased branches.

3. Fertilization
Taking greenhouse rose farming in Yunnan of China as an example, these roses grow year-round and require intensive cultivation. They need significant amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK) fertilizers. However, excessive use of chemical fertilizers can lead to soil salinization, acidification, and compaction, which severely affect cultivation.
To maintain a healthy rose garden, combine organic and inorganic fertilizers to ensure balanced nutrition. Use fertilizers with low residual metal salts. During the early growth stage, the NPK ratio should be 3:1:2. During the flowering stage, adjust it to 3:1:3. In addition to NPK, roses also need trace elements like calcium, magnesium, zinc, and boron, which should be added during cultivation.

Section 6: Harvesting and Post-Harvest Handling
Cut roses are prone to spoilage, making post-harvest management crucial. Maintaining a complete cold chain system (from production site, flower center, supermarket, to flower shop) and using specific preservation solutions are essential for extending the shelf life and quality of roses.

Here are some resources on harvesting and handling cut roses for your reference.
References
- Post harvesting and value addition in rose: Detailed information on post-harvest handling and value addition can be found in the study by Reji Longjam, Kiran Huirongbam, Sanam Kamboj, Ajay Singh Jakhar, and Sukhwinder Singh published in The Pharma Innovation.
- POST-HARVEST HANDLING OF CUT-FLOWER ROSE: Learn about effective post-harvest handling techniques in Subash Dahal’s work.
- POST-HARVESTING OF ROSES: Additional insights are available in the article by Communications in Plant Sciences, cv. Ipanema.
Section 7: Market and Sales Strategies
In addition to the ongoing growth in demand for roses, there is a significant surge in demand during holidays like Mother’s Day, Valentine’s Day, and Christmas. To meet this demand, it is crucial to plan ahead to ensure an adequate supply. By using advanced mathematical models like ROSGRO and ROSESIM, you can adjust production timing and resources in your greenhouse to align with market demand.
1. Cost Management
The cost of growing roses involves multiple factors, such as energy, labor, and facility management. For example, moving operations to countries with lower energy costs, like Tanzania and Kenya, can significantly increase profitability. In these regions, roses can be grown in low-cost plastic film greenhouses. Increasing greenhouse automation and optimizing labor costs are also effective ways to reduce expenses and improve efficiency.

2. Sales Strategies
To reduce transportation costs and ensure freshness, consider growing roses close to major markets. For instance, the Dounan Flower Market in Yunnan, China, is Asia’s largest and the world’s second-largest flower trading market, with cut roses accounting for about 70% of China’s total production. Being near such a market can enhance your competitiveness. Additionally, using online platforms and social media can expand your consumer base and increase brand exposure, especially during holiday promotions.

3. Profit Calculation
Profit = Total Revenue – Total Cost. Given that the price of roses can vary by season and region, you can estimate the potential profit from operating a greenhouse based on local market conditions.
Conclusion
Commercial rose cultivation involves many factors. Besides the topics we covered, you will also need to consider the operational costs after setting up the greenhouse. For building large greenhouses, consider importing from major manufacturing countries like China. Feel free to contact us for details on customization and the latest pricing.





